本教程是的一部分: ESP32-S3 RGB LED 点阵
这是一个很棒的项目,可以使用 ESP32-S3 RGB 矩阵模块进行创作,兼具趣味性和实用性。本文下方有其他相关视频的链接。
ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵项目5 - 箭头始终向上
项目 5 - 箭头始终向上(使用 QMI8658C 的方向指示器)
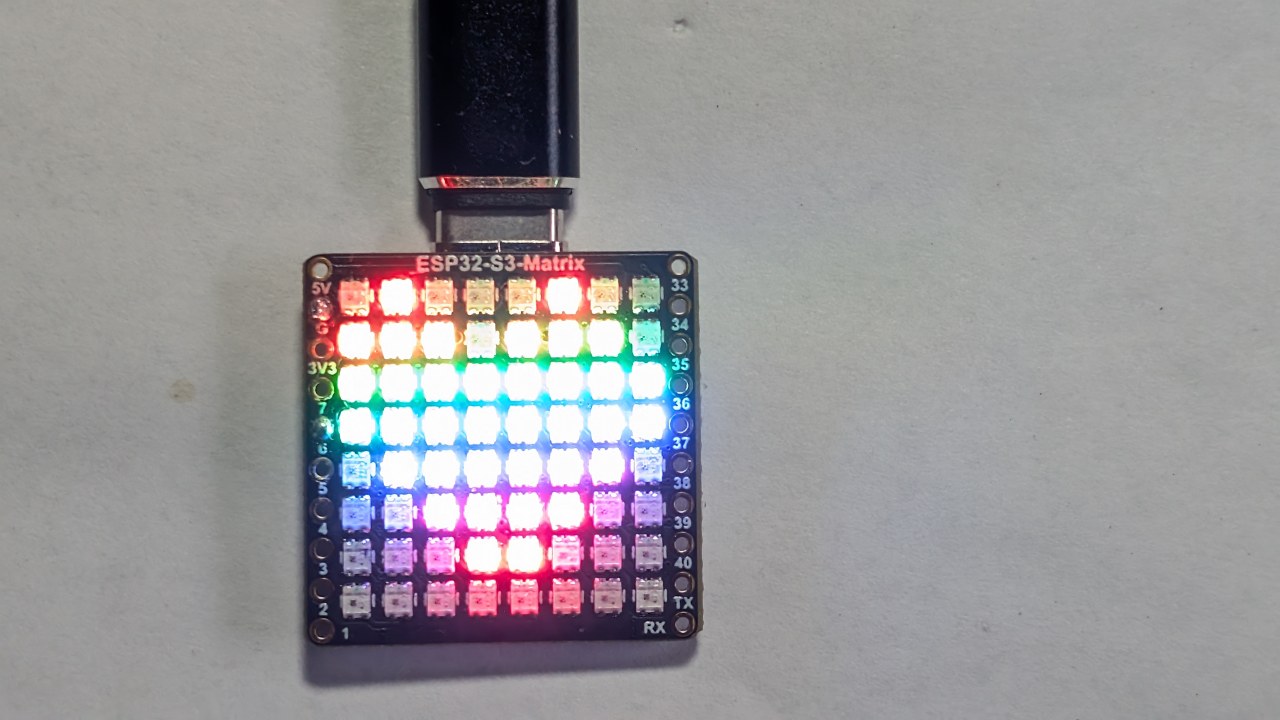
项目5使用QMI8658C运动传感器检测ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵的朝向,始终显示一个指向重力方向上的箭头。无论你怎么旋转电路板——USB侧朝上、OUSB侧朝上、侧面“15”或侧面“34”——箭头都会自动旋转并指向物理上的上方。
这是使用机载加速度计进行实时定向传感的强大演示。该模块的所有六个项目都在一个YouTube视频中演示,视频也嵌入在此页面上。项目5的完整代码会在文章下方自动加载,并且附属链接在代码部分下方出现。

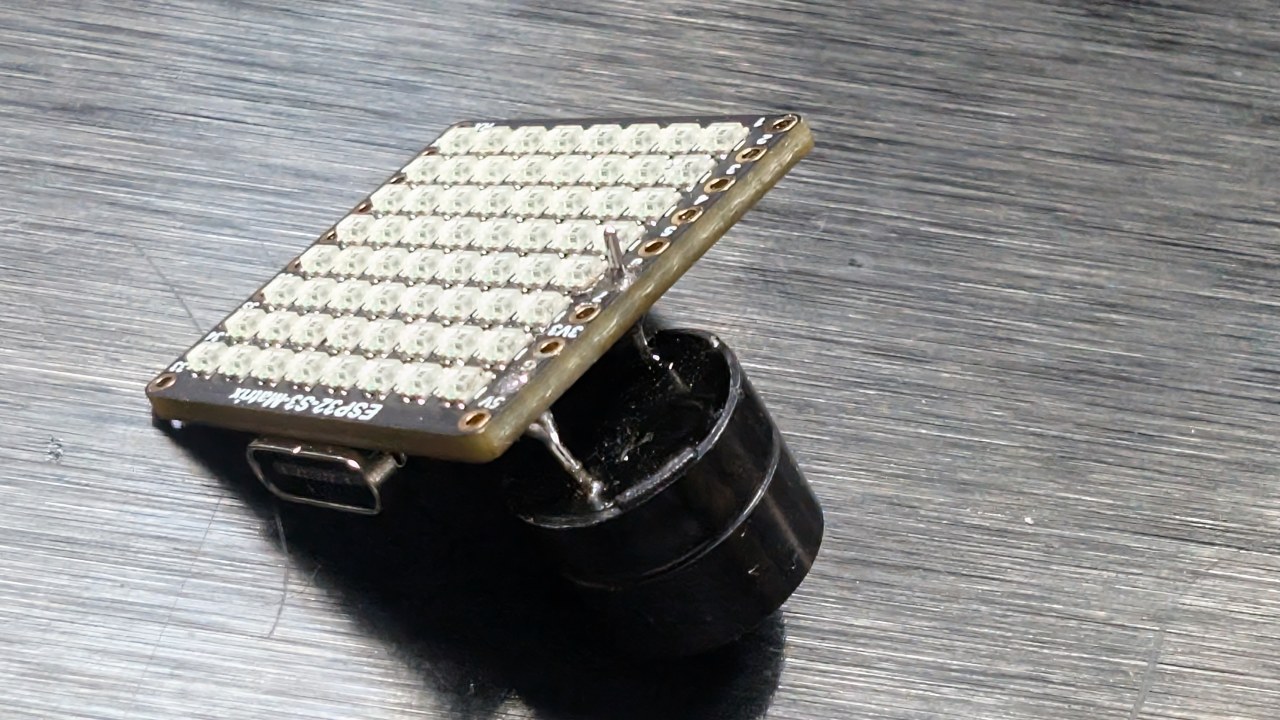
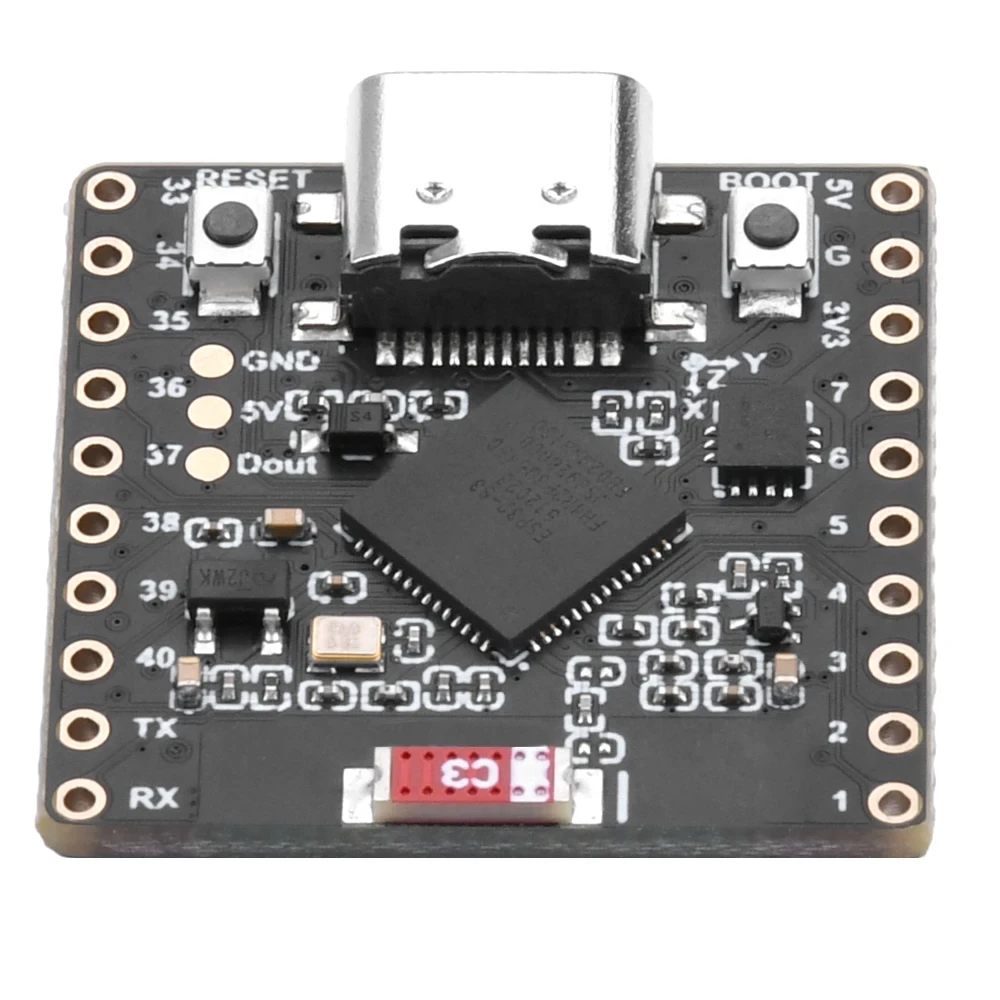
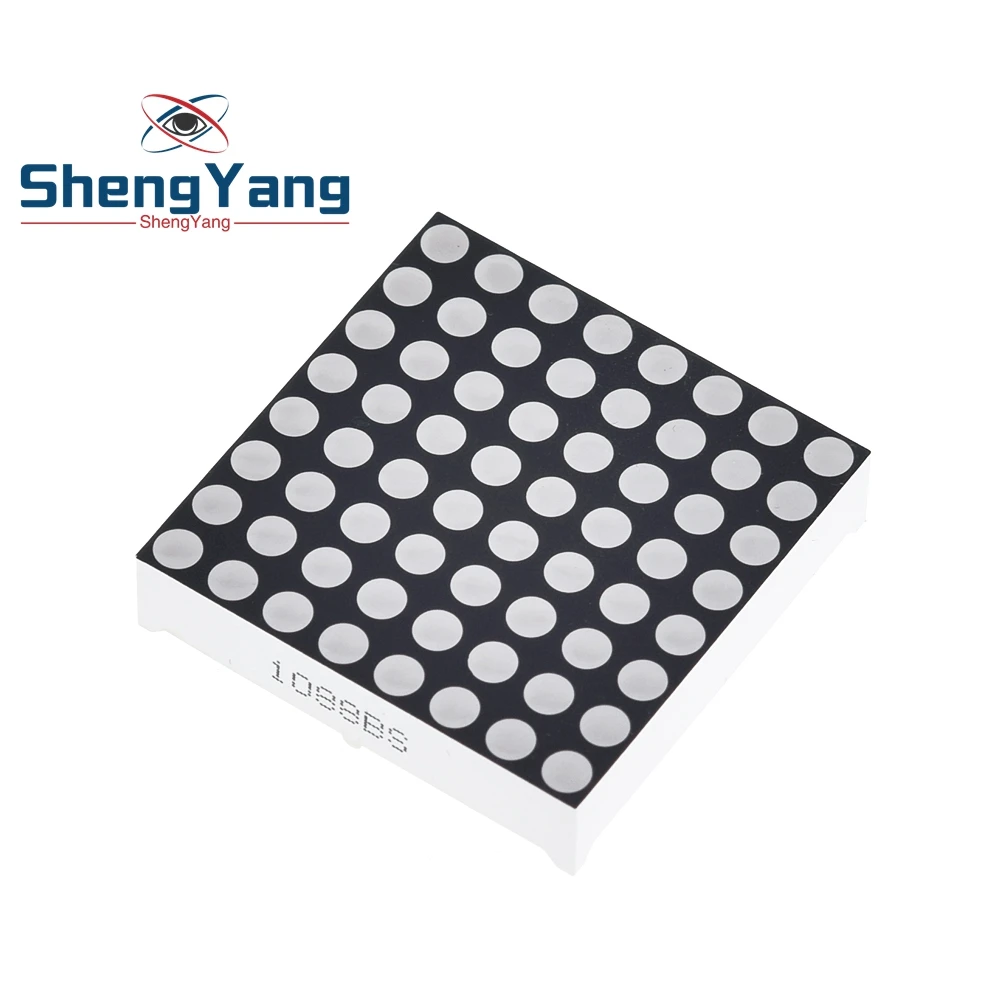
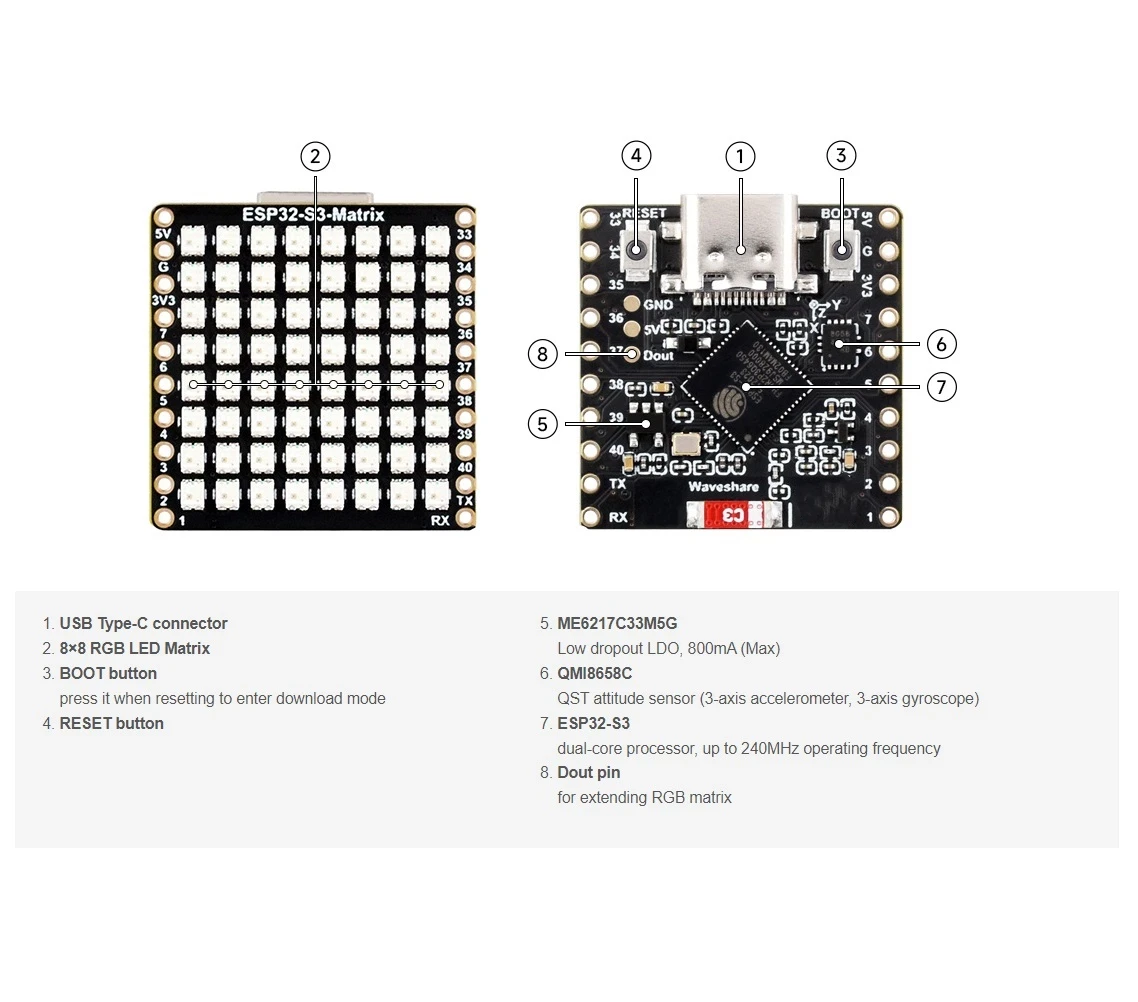
ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵模块概述
ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵模块包括几个使该项目成为可能的组件:
- ESP32-S3 微控制器- 提供 Wi-Fi、BLE,并运行 LED/IMU 逻辑。
- 8×8 RGB LED 矩阵- 在四个方向中显示箭头。
- QMI8658C 加速度计- 检测倾斜、运动和方向。:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
- USB-C端口用于Arduino IDE的电源和编程。
- 重置和启动按钮用于上传草图。
- GPIO引脚可用于其他项目的资源。
箭头方向完全由加速度计读数决定。当板子旋转时,QMI8658C 传感器感知新的 X/Y/Z 值,程序选择应该绘制哪个箭头图案 (↑, ↓, ←, →)。
视频中涵盖的项目(时间戳)
- 00:00- 介绍
- 02:01- 安装ESP32开发板
- 03:32安装库
- 05:32- 项目 1: 移动点
- 11:11- 项目 2:文本滚动
- 12:59- 项目 3:HTTP 文本
- 16:41- 项目 4:倾斜点
- 18:55-项目5:箭头始终向上(此项目)
- 20:02- 项目6:目标游戏
视频清楚地显示了箭头如何根据模块的转动瞬间改变方向。强烈建议观看这一部分。:contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}

在Arduino IDE中安装ESP32开发板
如果您完成了任何早期项目,董事会的设置已经完成。否则:
File > Preferences→ 添加ESP32板网址Tools > Board > Boards Manager…→ 安装 "ESP32"- 在下方选择ESP32-S3开发板
Tools > Board - 在下方选择正确的USB COM端口
Tools > Port
安装所需库
项目5使用:
Adafruit NeoMatrixAdafruit NeoPixelAdafruit GFXQMI8658(运动传感器)
Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries…- 搜索:新矩阵→ 安装
- 安装依赖项:NeoPixel+GFX
- 搜索并安装QMI8658由其作者编写
项目5如何运作
QMI8658C 在 X、Y 和 Z 轴上测量重力。通过比较这些值,草图确定电路板的哪个物理面朝上:
- USB面朝上
- OUSB面朝上(相对 USB)
- 侧面“15”朝上
- 面朝“34”向上
每个方向对应于8×8矩阵上的不同箭头图案。映射遵循您之前调试会话中确认的方向逻辑。棋盘的旋转持续读取,箭头会在向上侧变化时立即更新。
项目 5 - 代码设置(箭头始终向上)
以下是来自配置区域的用户可调值。完整的项目代码会在文章下方自动显示。
矩阵配置
// Matrix configuration
const int MATRIX_PIN = 14; // fixed for this module
const int MATRIX_WIDTH = 8;
const int MATRIX_HEIGHT = 8;
// Recommended orientation: Top-Left origin, progressive mode
// (actual constructor is inside the code loaded below)
该项目使用NEO_MATRIX_PROGRESSIVE布局以确保箭头根据实际移动正确指向。
亮度
uint8_t matrixBrightness = 40; // 0–255
您可以在光线较强的环境中提高此数值。在室内使用时,30-60是舒适的。
箭头颜色
// Arrow color
uint8_t arrowRed = 255;
uint8_t arrowGreen = 0;
uint8_t arrowBlue = 0;
更改这些值以修改箭头的颜色。例如:
- 绿色箭头:
(0, 255, 0) - 蓝色箭头:
(0, 0, 255) - 白色箭头:
(255, 255, 255)
灵敏度和平滑处理
为了避免抖动,代码包含平滑和阈值逻辑。在设置中,您可能会找到类似:
// Sensitivity / smoothing adjustment
float tiltThreshold = 0.30f; // adjust if arrow changes too easily
- 如果你的箭头翻转得太容易→增加阈值。
- 如果箭头变化太慢 →减少阈值。
箭头图案
草图包括箭头位图模式用于:
- ↑ 向上
- ↓ 下
- ← 左
- → 右
您无需修改这些,但如果您想要不同的风格,可以更改代码中的形状。
摘要
项目5展示了ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵和QMI8658C加速度计如何协同工作以检测方向,并显示一支始终向上的箭头。该项目基于倾斜点(项目4),为您在项目6中的最终互动游戏做好准备。
本文章下方提供完整的“箭头总是向上”草图(自动加载)。强烈建议观看视频中对应部分,以观察箭头如何瞬间响应电路板的旋转。如果您希望在家中构建此项目,ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵模块的关联链接在代码部分下方出现。
图像
本教程是……的一部分: ESP32-S3 RGB LED 点阵
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵项目 1- 基本点阵
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵项目2 - 滚动文字
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵项目3 - 手机文本
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵项目4 - 倾斜点
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵项目6 - Cible游戏
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED 矩阵 Wi-Fi + NTP 时钟项目 - 1 基本时钟
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵网络时钟项目 - 2个时钟多彩时间和日期显示
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵互联网时钟项目 - 带日期的3种夜间颜色
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED 矩阵网络时钟项目 - 5 种彩虹色
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵互联网时钟项目 - 4种随机颜色
- ESP32-S3 RGB LED矩阵测试,RGB,GRB设置
/*
Project 5: Arrow Always Up – ESP32-S3 RGB LED Matrix (Waveshare)
This sketch reads tilt from the QMI8658C IMU and smoothly moves a dot
on the 8×8 RGB LED matrix based on board orientation.
▶️ Video Tutorial:
https://youtu.be/JKLuYrRcLMI
📚⬇️ Resources & Code Page:
https://robojax.com/RJT833
QMI8658_RGB_2
*/
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoMatrix.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#include <QMI8658.h> // by Lahav Gahali
// -------- LED MATRIX SETUP --------
#define MATRIX_PIN 14
#define MATRIX_WIDTH 8
#define MATRIX_HEIGHT 8
Adafruit_NeoMatrix matrix = Adafruit_NeoMatrix(
MATRIX_WIDTH, MATRIX_HEIGHT, MATRIX_PIN,
NEO_MATRIX_TOP + NEO_MATRIX_LEFT +
NEO_MATRIX_ROWS + NEO_MATRIX_PROGRESSIVE,
NEO_RGB + NEO_KHZ800
);
// -------- QMI8658 IMU SETUP --------
QMI8658 imu;
QMI8658_Data imuData;
// -------- USER SETTINGS --------
// true -> arrow points to opposite side
// USB↔OUSB, 34↔15
// false -> arrow points to the same side that is UP
bool useOppositeMapping = false;
// Arrow color (0–255 each)
uint8_t dotRed = 0;
uint8_t dotGreen = 150;
uint8_t dotBlue = 0;
// Board sides
enum Side {
SIDE_CENTER = 0,
SIDE_USB,
SIDE_OUSB,
SIDE_15,
SIDE_34
};
// Direction for arrow drawing
enum ArrowDir {
ARROW_CENTER,
ARROW_UP,
ARROW_DOWN,
ARROW_LEFT,
ARROW_RIGHT
};
bool isFlat = false;
const char* sideName(Side s) {
switch (s) {
case SIDE_CENTER: return "CENTER";
case SIDE_USB: return "USB";
case SIDE_OUSB: return "OUSB";
case SIDE_15: return "15";
case SIDE_34: return "34";
default: return "?";
}
}
// -------- ARROW DRAWING (YOUR CODE, UNCHANGED) --------
// Draw a simple arrow on 8x8 matrix pointing in the given direction
void drawArrow(ArrowDir dir, uint16_t color) {
matrix.fillScreen(0);
switch (dir) {
case ARROW_UP:
// Tip
matrix.drawPixel(3, 0, color);
matrix.drawPixel(4, 0, color);
// Second row
matrix.drawPixel(2, 1, color);
matrix.drawPixel(3, 1, color);
matrix.drawPixel(4, 1, color);
matrix.drawPixel(5, 1, color);
// Shaft
matrix.drawLine(3, 2, 3, 6, color);
matrix.drawLine(4, 2, 4, 6, color);
break;
case ARROW_DOWN:
// Tip
matrix.drawPixel(3, 7, color);
matrix.drawPixel(4, 7, color);
// Row above tip
matrix.drawPixel(2, 6, color);
matrix.drawPixel(3, 6, color);
matrix.drawPixel(4, 6, color);
matrix.drawPixel(5, 6, color);
// Shaft
matrix.drawLine(3, 1, 3, 5, color);
matrix.drawLine(4, 1, 4, 5, color);
break;
case ARROW_LEFT:
// Tip
matrix.drawPixel(0, 3, color);
matrix.drawPixel(0, 4, color);
// Column after tip
matrix.drawPixel(1, 2, color);
matrix.drawPixel(1, 3, color);
matrix.drawPixel(1, 4, color);
matrix.drawPixel(1, 5, color);
// Shaft
matrix.drawLine(2, 3, 6, 3, color);
matrix.drawLine(2, 4, 6, 4, color);
break;
case ARROW_RIGHT:
// Tip
matrix.drawPixel(7, 3, color);
matrix.drawPixel(7, 4, color);
// Column before tip
matrix.drawPixel(6, 2, color);
matrix.drawPixel(6, 3, color);
matrix.drawPixel(6, 4, color);
matrix.drawPixel(6, 5, color);
// Shaft
matrix.drawLine(1, 3, 5, 3, color);
matrix.drawLine(1, 4, 5, 4, color);
break;
case ARROW_CENTER:
default:
// Simple plus in the center
matrix.drawLine(3, 3, 4, 3, color);
matrix.drawLine(3, 4, 4, 4, color);
matrix.drawLine(3, 3, 3, 4, color);
matrix.drawLine(4, 3, 4, 4, color);
break;
}
matrix.show();
}
// -------- IMU → SIDE DETECTION --------
// We calibrated earlier:
// +X = USB, -X = OUSB
// +Y = 15, -Y = 34 (after your correction)
Side detectSideUp(float ax_g, float ay_g, float az_g) {
// Flat detection
const float flatThreshXY = 0.15f;
const float flatThreshZ = 0.15f;
if (fabs(ax_g) < flatThreshXY &&
fabs(ay_g) < flatThreshXY &&
fabs(az_g - 1.0f) < flatThreshZ) {
isFlat = true;
return SIDE_CENTER;
}
isFlat = false;
// Thresholds to say "this axis is really tilted"
const float tiltThreshY = 0.5f;
const float tiltThreshX = 0.5f;
// Prefer Y axis for 15 / 34
if (fabs(ay_g) >= tiltThreshY) {
if (ay_g > 0) {
return SIDE_34; // +Y = 34 up
} else {
return SIDE_15; // -Y = 15 up
}
}
// Otherwise, use X axis for USB / OUSB
if (fabs(ax_g) >= tiltThreshX) {
if (ax_g > 0) {
return SIDE_USB; // +X = USB up
} else {
return SIDE_OUSB; // -X = OUSB up
}
}
// Not clearly tilted → treat as center
return SIDE_CENTER;
}
// Map from UP side to where the arrow should point
Side arrowSideFromUpSide(Side upSide) {
if (!useOppositeMapping) {
// Arrow shows the side that is UP
return upSide;
}
// Arrow shows the opposite side
switch (upSide) {
case SIDE_USB: return SIDE_OUSB;
case SIDE_OUSB: return SIDE_USB;
case SIDE_15: return SIDE_34;
case SIDE_34: return SIDE_15;
case SIDE_CENTER:
default: return SIDE_CENTER;
}
}
// Convert SIDE to ArrowDir
ArrowDir arrowDirFromSide(Side s) {
switch (s) {
case SIDE_USB: return ARROW_UP;
case SIDE_OUSB: return ARROW_DOWN;
case SIDE_15: return ARROW_LEFT;
case SIDE_34: return ARROW_RIGHT;
case SIDE_CENTER:
default: return ARROW_CENTER;
}
}
// ---------------- SETUP & LOOP ----------------
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(500);
matrix.begin();
matrix.setBrightness(20);
matrix.fillScreen(0);
matrix.show();
// IMU: SDA=11, SCL=12 on ESP32-S3-Matrix
if (!imu.begin(11, 12)) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize QMI8658!");
while (1) { delay(1000); }
}
imu.setAccelUnit_mg(true);
imu.setGyroUnit_dps(true);
imu.setDisplayPrecision(4);
Serial.print("QMI8658 initialized. useOppositeMapping = ");
Serial.println(useOppositeMapping ? "TRUE" : "FALSE");
}
void loop() {
if (!imu.readSensorData(imuData)) {
return;
}
float ax_g = imuData.accelX / 1000.0f;
float ay_g = imuData.accelY / 1000.0f;
float az_g = imuData.accelZ / 1000.0f;
Side upSide = detectSideUp(ax_g, ay_g, az_g);
Side arrowSide = arrowSideFromUpSide(upSide);
ArrowDir dir = arrowDirFromSide(arrowSide);
uint16_t color = matrix.Color(dotRed, dotGreen, dotBlue);
drawArrow(dir, color);
// Debug
Serial.print("AX="); Serial.print(ax_g, 3);
Serial.print(" AY="); Serial.print(ay_g, 3);
Serial.print(" AZ="); Serial.print(az_g, 3);
Serial.print(" | UP="); Serial.print(sideName(upSide));
Serial.print(" | ARROW="); Serial.println(sideName(arrowSide));
delay(80);
}
|||您可能需要的东西
-
亚马逊从亚马逊购买ESP32-S3 RGB矩阵amzn.to
-
易趣从eBay购买ESP32-S3 RGB矩阵ebay.us
-
全球速卖通从AliExpress购买ESP32-S3 RGB矩阵 (2)s.click.aliexpress.com
-
全球速卖通在AliExpress上购买ESP32-S3 RGB矩阵s.click.aliexpress.com
资源与参考
-
内部颜色选择器工具robojax.com
文件📁
Fritzing 文件
-
esp32-S3-supermini-tht Fritzing 部件
esp32-S3-supermini-tht.fzpz0.02 MB