This tutorial is part of: Controlling Relay Using Arduino
This is groups videos all related to relay. Links to other videos are below this article.
Using a 5V Relay Module (Low-Trigger) with Arduino
In this tutorial, we will explore how to use a 5V relay module with an Arduino, specifically focusing on a low-trigger relay. A relay allows you to control high voltage devices with a low voltage microcontroller, making it an essential component for various automation projects. By the end of this tutorial, you'll be able to turn a relay on and off using your Arduino, which can be applied to control lights, motors, and other devices.

To achieve this, we will write a simple Arduino program that toggles the relay on and off at regular intervals. This project is straightforward and ideal for beginners looking to understand how relays work with microcontrollers (in video at 00:30).
Load Power Rating
The power rating of your 5V relay, labeled for 10 amperes, is not determined by its own coil voltage but by the maximum current it can safely switch for the load (device) you are controlling. The "5V" refers to the voltage required to energize the relay's coil, while the "10A" is its contact rating—the maximum current the internal switch can handle. To calculate the maximum load power (in watts) the relay can connect or disconnect, you multiply the relay's current rating (10A) by the voltage of the circuit you are switching. For instance, switching a 100V AC mains device: 10A × 100V = 1000W. For a 12V DC car accessory: 10A × 12V = 120W. Crucially, you must always ensure the voltage of the circuit you are switching does not exceed the relay's specified maximum contact voltage, which is a separate, higher rating (e.g., 250V AC) listed in its datasheet. Therefore, your relay can control any load up to 10A, provided the load's voltage is within the relay's contact voltage limits, and you calculate the corresponding wattage from there.
Hardware Explained
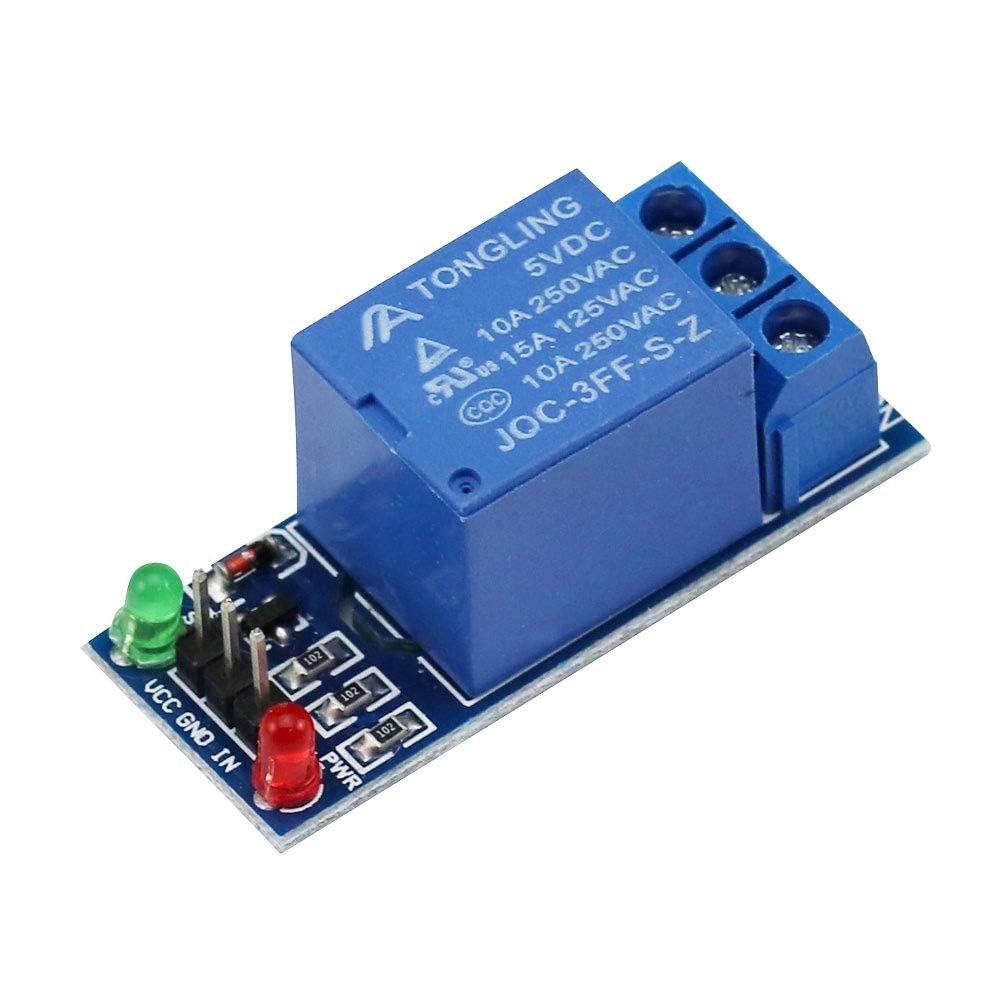
The main components required for this project include an Arduino board, a 5V relay module, and jumper wires. The Arduino board serves as the brain of the operation, sending signals to the relay module to control its state. The relay module is designed to switch devices on or off by controlling the high voltage side with a low voltage signal from the Arduino.
Each relay module typically includes an opto-isolator for isolation between the low voltage and high voltage circuits, protecting the Arduino from back EMF and voltage spikes. In our case, we will be using a low-trigger relay, meaning that it is activated when the control signal is set to LOW.


What is a relay?
A relay is an electromagnetic switch that uses a small electric current to control a much larger one, safely isolating different parts of a circuit. As shown in the diagrams, it has two main parts: the coil and the contacts. When you connect the 5V battery through the small switch, electricity flows through the relay's coil. This turns the coil into an electromagnet, which physically pulls the internal switch—the contacts—closed. This action connects a separate, high-power circuit. In essence, the tiny 5V signal from the battery and switch acts as a remote control, allowing you to use a safe, low-voltage circuit to turn on and off a powerful, high-voltage device without the two currents ever mixing directly.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | Generic |
|---|---|
| Part number | 5V Relay Module |
| Control Voltage | 5 V |
| Relay Type | Low-Trigger |
| Max Load Voltage | 250 V AC / 30 V DC |
| Max Load Current | 10 A |
| Opto-Isolation | Yes |
| Package | Module |
- Ensure proper heat dissipation when using high loads.
- Use a separate power supply for high voltage devices.
- Double-check wiring to avoid short circuits.
- Confirm the relay's specifications match your intended load.
- Test the relay with a multimeter before connecting high voltage.
Wiring Instructions
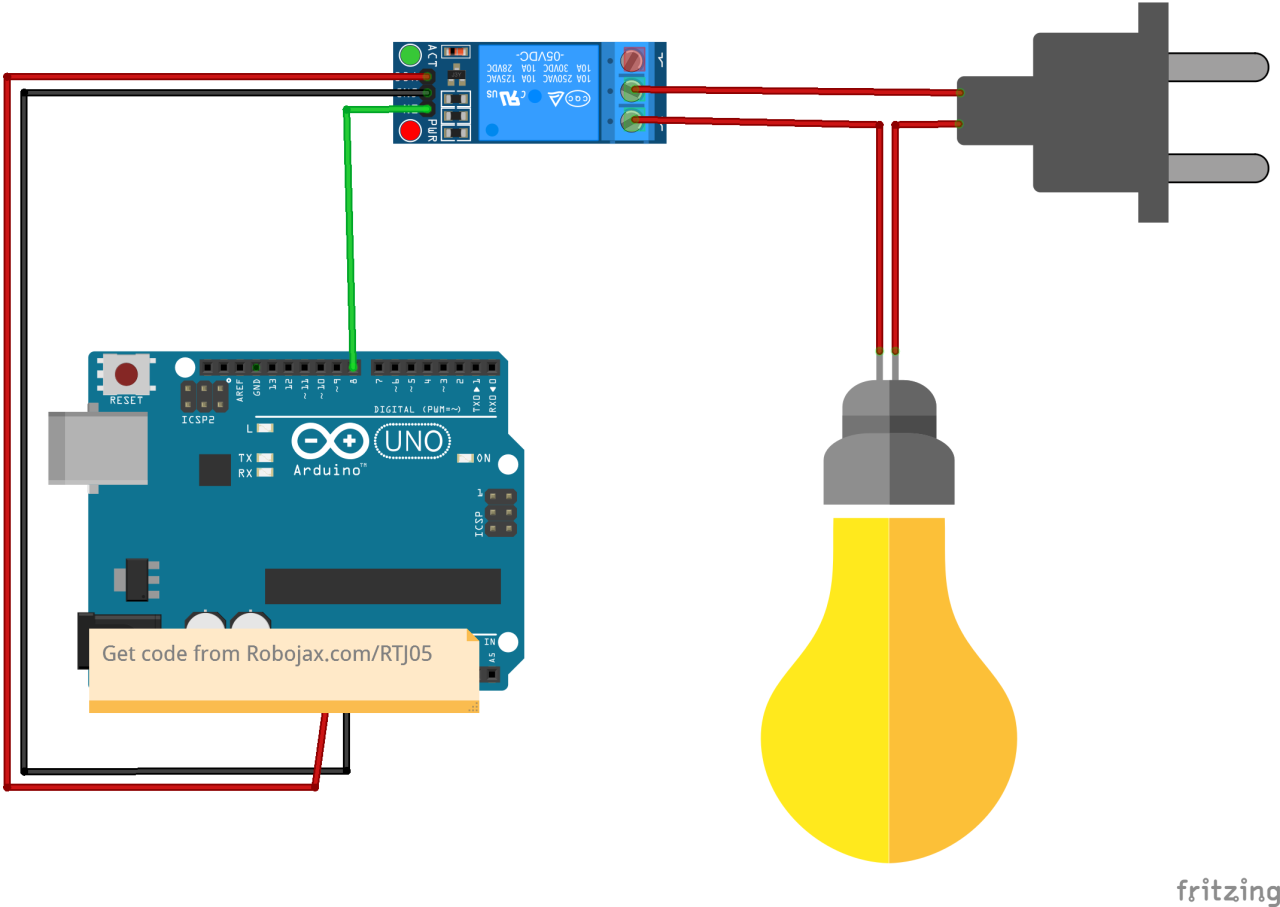
To wire the relay module, start by connecting the VCC pin of the relay module to the 5V pin on the Arduino. Then, connect the GND pin of the relay module to the GND pin on the Arduino. The control pin for the relay, often labeled as IN, should be connected to a digital pin on the Arduino, for example, pin 8. This setup allows the Arduino to control the relay state.
Once the wiring is complete, you will have the VCC and GND providing power to the relay module, while the control pin will send signals to turn the relay on and off. Ensure that the connections are secure to prevent any intermittent issues during operation. If you are using a different Arduino board, make sure to map the control pin accordingly.
Code Examples & Walkthrough
int relayPin = 8; // define output pin for relay
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // define pin 8 as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // turn the relay ON
delay(500); // wait for 500 milliseconds
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // turn the relay OFF
delay(500); // wait for 500 milliseconds
}
In the code, we start by defining the output pin for the relay with relayPin set to 8. In the setup() function, we configure this pin as an OUTPUT. The loop() function continuously toggles the relay state by writing LOW to the pin, turning it ON, and then writing HIGH, turning it OFF after a 500-millisecond delay.
Demonstration / What to Expect
Once the wiring and programming are complete, you should observe the relay clicking on and off every half second. This indicates that the Arduino is successfully controlling the relay. If you connect a high voltage device to the relay, it should turn on and off in sync with the relay's state. Ensure that the relay is rated for the voltage and current of the device you are controlling to prevent damage (in video at 02:15).
Common pitfalls include incorrect wiring, which can lead to the relay not functioning as expected. Additionally, ensure that you are using a low-trigger relay; otherwise, you may need to adjust the code to accommodate a high-trigger relay.
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 Introduction to the project
- 00:30 Hardware overview
- 01:15 Wiring instructions
- 02:15 Demonstration of the relay in action
This tutorial is part of: Controlling Relay Using Arduino
- Arduino Code and Video for a Dual-Channel 5V Relay
- Controlling a 5V Relay Using Arduino to cotrol AC or DC load like bulb or motor
- TTP224 4-Channel Touch Sensor to Turn AC/DC Loads with Relay
- Using a MAX6675 K-Type Thermocouple with Relay and Display
- Using a Reed Switch to Control a Relay and AC/DC Loads with an Arduino
- Using a TTP223B touch module and relay to control AC/DC loads with an Arduino
- Using an Arduino push button to switch a relay and AC bulb
// April 1, 2017
// Written by Ahmad Shamshiri for Robojax.com video
// Introduction to 5V relay.
// Watch video for this code: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7tUGUXyloXQ
/*
* Please keep this note with the code.
* This code is available on Robojax.com
*
* This code is "AS IS" without warranty or liability. Free to be used as long as you keep this note intact.
* This code has been downloaded from Robojax.com
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
int relayPin = 8;// define output pin for relay
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT);// define pin 8 as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // turn the relay ON (low is ON if relay is LOW trigger. Change it to HIGH if you have a HIGH trigger relay)
delay(500); // wait for 500 milliseconds
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);// // turn the relay OFF (HIGH is OFF if relay is LOW trigger. Change it to LOW if you have a HIGH trigger relay)
delay(500);// wait for 500 milliseconds
}Resources & references
No resources yet.
Files📁
Fritzing File
-
5V Relay Module_LOW_trigger
5V Relay Module_LOW_trigger.fzpz0.08 MB -
5V RELAY 2.0
5V RELAY 2.0.fzpz0.02 MB


![Arduino Uno REV3 [A000066] - ATmega328P Microcontroller, 16MHz, 14 Digital I/O Pins, 6 Analog Inputs, 32KB Flash, USB Connectivity, Compatible with Arduino IDE for DIY Projects and Prototyping](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/515P6aYSP4L._SL75_.jpg)
![Arduino UNO Q 2-GB RAM [ABX00162] - Hybrid Board, Qualcomm Dragonwing QRB2210 microprocessor (MPU) & STM32U585 Microcontroller(MCU), AI Vision, Voice, IoT, Robotics, Linux Debian OS, Wi-Fi 5, USB-C](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51RF8Jz8UOL._SL75_.jpg)


![Official Arduino Starter Kit [K000007] - 12 DIY Projects with Electronic Components & English Projects Book - Original Kit from Italy](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51fPv6DsjQL._SL75_.jpg)