Measuring Distance with a Laser VL53L0X 6-Pin Module for Arduino
In this tutorial, we will learn how to measure distance using the VL53L0X laser distance sensor with a 6-pin module. This small yet powerful sensor utilizes time-of-flight technology to provide accurate distance measurements up to 200 cm. By following this guide, you will be able to set up the sensor with an Arduino and read distance values directly from your serial monitor.

For this project, we will be using the VL53L0X sensor, which is compact and easy to integrate into various applications. The sensor communicates via I2C, making it simple to connect to an Arduino board. In the video, you'll find additional explanations and demonstrations of the setup process (in video at 04:00).
Hardware Explained
The VL53L0X is a time-of-flight distance sensor that emits a laser beam and measures the time it takes for the light to return after hitting an object. This allows it to calculate the distance to the object accurately. The sensor operates at a voltage between 2.6 V to 3.5 V, but it can be powered with 5 V thanks to an internal voltage regulator.
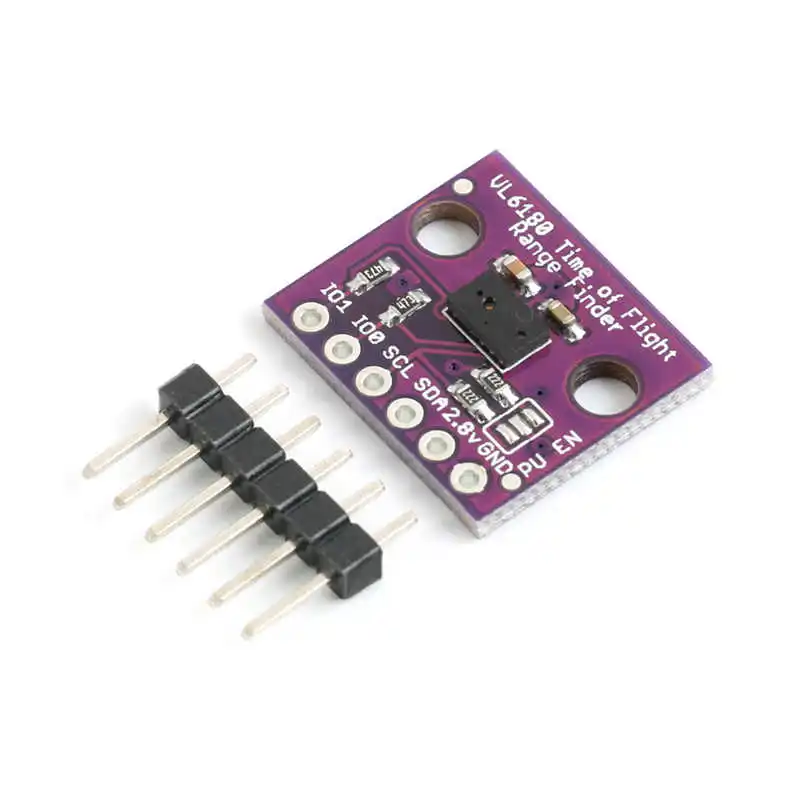
The module has six pins: VCC, GND, SDA (data line), SCL (clock line), GPIO1 (general-purpose I/O), and XSHUT (shutdown pin). The GPIO1 pin is not used in this configuration but can be left unconnected. The XSHUT pin allows you to shut the sensor down to save power when not in use.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | STMicroelectronics |
|---|---|
| Part number | VL53L0X |
| Logic/IO voltage | 2.6 V to 3.5 V (5 V with regulator) |
| Operating temperature | -20 °C to 70 °C |
| Measurement range | 30 mm to 2000 mm |
| I2C communication frequency | 400 kHz |
| Size | 4.4 mm x 2.4 mm x 1 mm |
- Ensure proper power supply (5 V recommended).
- Connect SDA and SCL to the appropriate I2C pins on the Arduino.
- Use pull-up resistors on the I2C lines if required.
- Do not leave GPIO1 unconnected; it can be left floating.
- Keep the XSHUT pin high during operation.
- Measure distances in a well-lit environment for better accuracy.
- Calibrate the sensor for accurate measurements.
- Test the sensor range by placing objects at various distances.
- Monitor the serial output for distance readings and timeout messages.
Wiring Instructions

To wire the VL53L0X sensor to your Arduino, start by connecting the VCC pin of the sensor to the 5V pin on the Arduino. Next, connect the GND pin to the GND on the Arduino. The SDA pin of the sensor should be connected to the A4 pin on the Arduino (or the SDA pin if your board has dedicated I2C pins). Likewise, connect the SCL pin of the sensor to the A5 pin (or the SCL pin). Leave the GPIO1 pin unconnected as it is not needed for this project.
Finally, connect the XSHUT pin to digital pin 12 on the Arduino. This pin will be used to control the shutdown state of the sensor. Make sure all connections are secure to avoid any communication issues.
Code Examples & Walkthrough
In the code, we begin by including the necessary libraries and initializing the VL53L0X sensor. The setup function configures the sensor and starts continuous distance measurements. Here is a snippet from the setup function:
void setup() {
pinMode(12, INPUT_PULLUP);
digitalWrite(12, HIGH);
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
sensor.init();
sensor.setTimeout(500);
sensor.startContinuous();
}In this snippet, we set pin 12 as an input with a pull-up resistor and initialize the serial communication at 9600 baud. We also initialize the sensor and set a timeout for readings, ensuring it operates continuously.
Next, we read the distance in the loop function, where the measured value is printed to the serial monitor:
void loop() {
int distance = sensor.readRangeContinuousMillimeters();
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.print("mm");
if (sensor.timeoutOccurred()) { Serial.print(" TIMEOUT"); }
Serial.println();
delay(100);
}This code reads the distance in millimeters and prints it to the serial monitor. If a timeout occurs, it indicates that the sensor did not receive a valid reading.
Demonstration / What to Expect
When you run the program, you should start seeing distance measurements on the serial monitor. The output will fluctuate as you move objects closer or further away from the sensor. You may notice occasional timeout messages if the sensor fails to get a reading (in video at 10:30). To improve accuracy, consider averaging multiple readings.
/* This example shows how to use continuous mode to take
range measurements with the 6-pin VL53L0X module. It is based on
vl53l0x_ContinuousRanging_Example.c from the VL53L0X API.
The range readings are in units of mm.
Original source: https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_VL53L0X
Modified by Ahmad Shamshiri for RoboJax.com/RJT83
Date modified: May 31, 2018 at 19:25 in Ajax, Ontario, Canada
Watch the instruction video for this code https://youtu.be/S2jaAQEv3Yo
Pin connection
VL53L0X Pin Arduino Pin
VCC 5V
GND GND
SDA A4 or SDA if available
SCL A5 or SCL if available
GPIO1 leave it unconnected
XSHUT D12 (digital 12 or pin 12)
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <VL53L0X.h>
VL53L0X sensor;
void setup()
{
pinMode(12,INPUT_PULLUP);
digitalWrite(12,HIGH);
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
sensor.init();
sensor.setTimeout(500);
// Start continuous back-to-back mode (take readings as
// fast as possible). To use continuous timed mode
// instead, provide a desired inter-measurement period in
// ms (e.g. sensor.startContinuous(100)).
sensor.startContinuous();
}
void loop()
{
int distance =sensor.readRangeContinuousMillimeters();
//int distance =sensor.startContinuous(100);
//distance = distance;
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.print("mm");
if (sensor.timeoutOccurred()) { Serial.print(" TIMEOUT"); }
Serial.println();
delay(100);
}|||您可能需要的东西
-
易趣从eBay购买VL53l0xebay.us
-
全球速卖通从AliExpress购买1至10个VL53L0X。s.click.aliexpress.com
-
Banggood从Banggood购买1到10个VL53L0X。banggood.com
资源与参考
-
外部从AliExpress购买1至10个VL53L0X。s.click.aliexpress.com
-
外部从Banggood购买1到10个VL53L0X。banggood.com
-
外部从eBay购买VL53l0xebay.us
-
外部在亚马逊购买VL53L0Xamzn.to
文件📁
Fritzing 文件
-
VL53L0X_距离传感器_方块
VL53L0X_Distance_sensor_Squares.fzpz0.02 MB
其他文件
-
VL53L0X_距离传感器_紫色
VL53L0X_Distance_sensor_purple.fzpz0.01 MB