How to Use an Allegro ACS758 Current Sensor with Arduino for 50A to 200A
Current measurement in high-capacity applications can be challenging, but the Allegro ACS758 current sensor simplifies this task. This sensor can handle current levels from 50A to 200A, providing a reliable solution for various projects. In this tutorial, we will explore how to connect the ACS758 to an Arduino and read current values accurately.

Hardware Explained
The main component in this project is the Allegro ACS758 current sensor. This sensor operates on the principle of the Hall effect, which allows it to measure the magnetic field generated by the current flowing through a conductor. It produces an output voltage proportional to the current, enabling the Arduino to read and interpret these values. The ACS758 has several variants, with the "100B" indicating that it can measure up to 100A. It features bi-directional current measurement, allowing for accurate readings regardless of the current direction. The sensor requires a power supply of 3.3V or 5V, which powers its internal circuitry, including an operational amplifier that processes the Hall effect signal.Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | Allegro Microsystems |
|---|---|
| Part number | ACS758LCB-100B |
| Logic/IO voltage | 3.3 V / 5 V |
| Supply voltage | 4.5 V - 5.5 V |
| Output current (per channel) | 100 A |
| Peak current (per channel) | 200 A |
| PWM frequency guidance | N/A |
| Input logic thresholds | TTL compatible |
| Voltage drop / RDS(on) / saturation | 0.1 V @ 100 A |
| Thermal limits | Operating temperature: -40 °C to 125 °C |
| Package | 5-pin package |
| Notes / variants | Available in different current ratings (50A, 100A, 150A, 200A) |
- Ensure proper wiring to avoid voltage drop due to resistance.
- Use appropriate gauge wire for high current applications to prevent overheating.
- Keep the sensor within specified temperature limits for accurate readings.
- Calibrate the sensor output based on the specific model used.
- Consider using filtering capacitors to stabilize readings if necessary.
Wiring Instructions
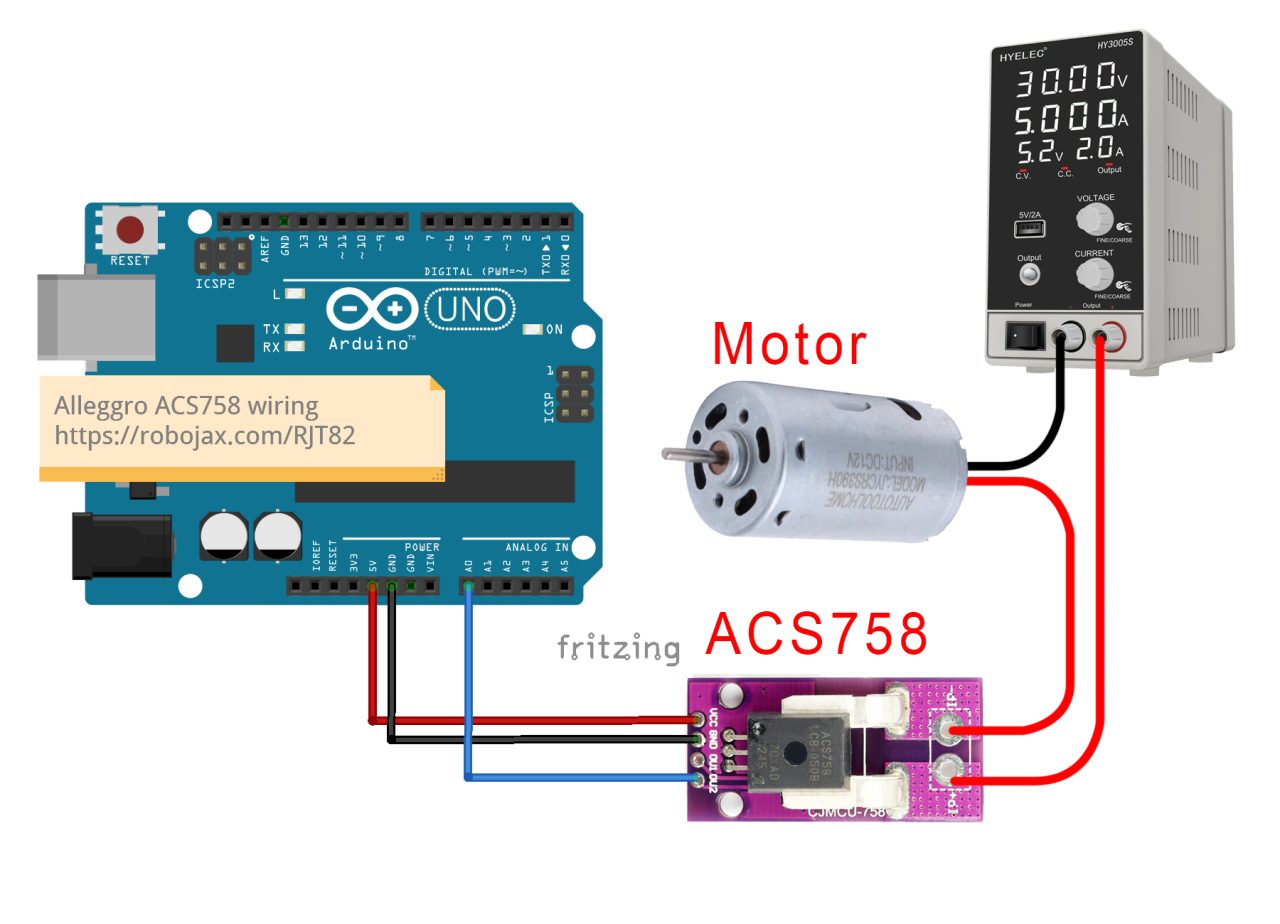
A0.
Ensure that the load you wish to measure is connected in series with the sensor. The current path should flow through the sensor so that it can accurately measure the current passing through it. The sensor has two current input pins; connect your load's positive wire to one of these pins and the other pin to your power supply's positive terminal. The negative side of the power supply should connect to the load's negative terminal. This setup allows the sensor to measure the current flowing to the load.
Code Examples & Walkthrough
The Arduino code for reading values from the ACS758 sensor is straightforward. Below is an excerpt from the advanced code that initializes the sensor and reads the voltage:
#define VIN A0 // define the Arduino pin A0 as voltage input (V in)
const float VCC = 5.0; // supply voltage
const float FACTOR = 20.0 / 1000; // sensitivity for the ACS758-100B
void loop() {
float voltage_raw = (5.0 / 1023.0) * analogRead(VIN); // Read the voltage from sensor
float current = (voltage_raw - (VCC * 0.5)) / FACTOR; // Calculate current
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.println(current, 2); // Print current value
}
Demonstration / What to Expect
Once everything is wired correctly and the code is uploaded, you should see current values displayed on the serial monitor. The readings will update every half second as defined in the code. If the current is below the cutoff limit set in the code, you will see a "No Current" message displayed. This cutoff helps filter out noise and small variations in current readings. Be cautious of reversed polarity connections, as this can damage the sensor. Always ensure that the sensor is correctly wired in series with the load, and monitor the output to confirm accurate readings. The video provides additional context and demonstrations (in video at 12:30).
100-Advanced Arduino code for the Allegro ACS758 current sensor
言語: C++
/*
*
* Arduino Sketch for Allegro ACS758 Current Sensor (Advanced)
* This sensor can measure current at a range of up to 200A.
* It operates with 3.3V or 5V.
* Please watch the video instruction and explanation for this code.
*
* Written by Ahmad Shamshiri on Saturday, May 27, 2018 at 13:19 in Ajax, Ontario, Canada
* for Robojax.com
* View the video instruction at
* This code has been downloaded from Robojax.com
*/
#define VIN A0 // define the Arduino pin A0 as voltage input (V in)
const float VCC = 5.0;// supply voltage 5V or 3.3V. If using PCB, set to 5V only.
const int model = 2; // enter the model (see below)
float cutOffLimit = 1.00;// reading cutoff current. 1.00 is 1 Ampere
/*
"ACS758LCB-050B",// for model use 0
"ACS758LCB-050U",// for model use 1
"ACS758LCB-100B",// for model use 2
"ACS758LCB-100U",// for model use 3
"ACS758KCB-150B",// for model use 4
"ACS758KCB-150U",// for model use 5
"ACS758ECB-200B",// for model use 6
"ACS758ECB-200U"// for model use 7
// sensitivity array is holding the sensitivity of the ACS758
// current sensors. Do not change.
*/
float sensitivity[] ={
40.0,// for ACS758LCB-050B
60.0,// for ACS758LCB-050U
20.0,// for ACS758LCB-100B
40.0,// for ACS758LCB-100U
13.3,// for ACS758KCB-150B
16.7,// for ACS758KCB-150U
10.0,// for ACS758ECB-200B
20.0,// for ACS758ECB-200U
};
/*
* Quiescent output voltage is a factor of VCC that appears at the output
* when the current is zero.
* For bidirectional sensors, it is 0.5 x VCC.
* For unidirectional sensors, it is 0.12 x VCC.
* For model ACS758LCB-050B, the B at the end represents Bidirectional (polarity doesn't matter).
* For model ACS758LCB-100U, the U at the end represents Unidirectional (polarity must match).
* Do not change.
*/
float quiescent_Output_voltage [] ={
0.5,// for ACS758LCB-050B
0.12,// for ACS758LCB-050U
0.5,// for ACS758LCB-100B
0.12,// for ACS758LCB-100U
0.5,// for ACS758KCB-150B
0.12,// for ACS758KCB-150U
0.5,// for ACS758ECB-200B
0.12,// for ACS758ECB-200U
};
const float FACTOR = sensitivity[model]/1000;// set sensitivity for selected model
const float QOV = quiescent_Output_voltage [model] * VCC;// set quiescent Output voltage for selected model
float voltage;// internal variable for voltage
float cutOff = FACTOR/cutOffLimit;// convert current cut off to mV
void setup() {
//Robojax.com ACS758 Current Sensor
Serial.begin(9600);// initialize serial monitor
Serial.println("Robojax Tutorial");
Serial.println("ACS758 Current Sensor");
}
void loop() {
//Robojax.com ACS758 Current Sensor
float voltage_raw = (5.0 / 1023.0)* analogRead(VIN);// Read the voltage from sensor
voltage = voltage_raw - QOV + 0.007 ;// 0.007 is a value to make voltage zero when there is no current
float current = voltage / FACTOR;
if(abs(voltage) > cutOff ){
Serial.print("V: ");
Serial.print(voltage,3);// print voltage with 3 decimal places
Serial.print("V, I: ");
Serial.print(current,2); // print the current with 2 decimal places
Serial.println("A");
}else{
Serial.println("No Current");
}
delay(500);
}101-Arduino code for Allegro ACS758 current sensor (basic)
言語: C++
/*
* Arduino Sketch for Allegro ACS758 Current Sensor (Basic Simple)
* This sensor can measure current at a range of up to 200A.
* It operates with 3.3V or 5V (the module works with 5V, the sensor can work with 3.3V or 5V).
* Please watch the video instruction and explanation for this code.
*
* Written by Ahmad Shamshiri on Saturday, May 26, 2018 at 7:05 PM in Ajax, Ontario, Canada
* for Robojax.com
* View the video instruction at https://youtu.be/SiHfjzcqnU4
* This code has been downloaded from Robojax.com
*/
#define VIN A0
const float vcc = 5.00;// supply voltage 5V or 3.3V
const float factor = 0.02;// 20mV/A is the factor
float voltage;
void setup() {
//Robojax.com ACS758 Current Sensor
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Robojax Tutorial");
Serial.println("ACS758 Current Tester");
Serial.println("Basic Simple Code");
}
void loop() {
//Robojax.com ACS758 Current Sensor
voltage = (5.0 / 1023.0)* analogRead(VIN);// Read the voltage from sensor
voltage = voltage - (vcc * 0.5) + 0.007 ;// 0.007 is a value to make voltage zero when there is no current
float current = voltage / factor;
Serial.print("V: ");
Serial.print(voltage,3);
Serial.print("V, I: ");
Serial.print(current,2); Serial.println("A");
delay(500);
}102-Advanced Arduino code for four Allegro ACS758 current sensors
言語: C++
/*
*
* Arduino Sketch for 4 modules Allegro ACS758 Current Sensor (Advanced)
* This sensor can measure current at a range of up to 200A.
* It operates with 3.3V or 5V.
* Please watch the video instruction and explanation for this code.
*
* Written by Ahmad Shamshiri on August 4, 2018 at 13:19 in Ajax, Ontario, Canada
* for Robojax.com in request from Ross M. from YouTube video https://youtu.be/SiHfjzcqnU4
* View the video instruction at
* This code has been downloaded from Robojax.com
*/
#define VIN1 A0 // define the Arduino pin A0 as voltage input (V in)
#define VIN2 A1
#define VIN3 A2
#define VIN4 A3
const float VCC = 5.0;// supply voltage 5V or 3.3V. If using PCB, set to 5V only.
const int model = 2; // enter the model (see below)
float cutOffLimit = 1.00;// reading cutoff current. 1.00 is 1 Amper
/*
"ACS758LCB-050B",// for model use 0
"ACS758LCB-050U",// for model use 1
"ACS758LCB-100B",// for model use 2
"ACS758LCB-100U",// for model use 3
"ACS758KCB-150B",// for model use 4
"ACS758KCB-150U",// for model use 5
"ACS758ECB-200B",// for model use 6
"ACS758ECB-200U"// for model use 7
sensitivity array is holding the sensitivity of the ACS758
current sensors. Do not change.
*/
float sensitivity[] ={
40.0,// for ACS758LCB-050B
60.0,// for ACS758LCB-050U
20.0,// for ACS758LCB-100B
40.0,// for ACS758LCB-100U
13.3,// for ACS758KCB-150B
16.7,// for ACS758KCB-150U
10.0,// for ACS758ECB-200B
20.0,// for ACS758ECB-200U
};
/*
* Quiescent output voltage is a factor of VCC that appears at the output
* when the current is zero.
* For bidirectional sensors it is 0.5 x VCC
* For unidirectional sensors it is 0.12 x VCC
* For model ACS758LCB-050B, the B at the end represents bidirectional (polarity doesn't matter).
* For model ACS758LCB-100U, the U at the end represents unidirectional (polarity must match).
* Do not change.
*/
float quiescent_Output_voltage [] ={
0.5,// for ACS758LCB-050B
0.12,// for ACS758LCB-050U
0.5,// for ACS758LCB-100B
0.12,// for ACS758LCB-100U
0.5,// for ACS758KCB-150B
0.12,// for ACS758KCB-150U
0.5,// for ACS758ECB-200B
0.12,// for ACS758ECB-200U
};
const float FACTOR = sensitivity[model]/1000;// set sensitivity for selected model
const float QOV = quiescent_Output_voltage [model] * VCC;// set quiescent Output voltage for selected model
float voltage1;// internal variable for voltage1
float voltage2;// internal variable for voltage2
float voltage3;// internal variable for voltage3
float voltage4;// internal variable for voltage4
float cutOff = FACTOR/cutOffLimit;// convert current cut off to mV
void setup() {
//Robojax.com ACS758 Current Sensor
Serial.begin(9600);// initialize serial monitor
Serial.println("Robojax Tutorial");
Serial.println("Four ACS758 Current Sensors");
}
void loop() {
//Robojax.com ACS758 Current Sensor
float voltage_raw1 = (5.0 / 1023.0)* analogRead(VIN1);// Read the voltage from sensor
float voltage_raw2 = (5.0 / 1023.0)* analogRead(VIN2);// Read the voltage from sensor
float voltage_raw3 = (5.0 / 1023.0)* analogRead(VIN3);// Read the voltage from sensor
float voltage_raw4 = (5.0 / 1023.0)* analogRead(VIN4);// Read the voltage from sensor
voltage1 = voltage_raw1 - QOV + 0.007 ;// 0.007 is a value to make voltage zero when there is no current
voltage2 = voltage_raw2 - QOV + 0.007 ;// 0.007 is a value to make voltage zero when there is no current
voltage3 = voltage_raw3 - QOV + 0.007 ;// 0.007 is a value to make voltage zero when there is no current
voltage4 = voltage_raw4 - QOV + 0.007 ;// 0.007 is a value to make voltage zero when there is no current
float current1 = voltage1 / FACTOR;
float current2 = voltage2 / FACTOR;
float current3 = voltage3 / FACTOR;
float current4 = voltage4 / FACTOR;
if(abs(voltage1) > cutOff ){ //Corrected abs(voltage) to abs(voltage1)
Serial.print("I1: ");
Serial.print(current1,2); // print the current with 2 decimal places
Serial.println("A");
Serial.print("I2: ");
Serial.print(current2,2); // print the current with 2 decimal places
Serial.println("A");
Serial.print("I3: ");
Serial.print(current3,2); // print the current with 2 decimal places
Serial.println("A");
Serial.print("I4: ");
Serial.print(current4,2); // print the current with 2 decimal places
Serial.println("A");
}else{
Serial.println("No Current");
}
delay(500);
}必要かもしれないもの
-
アマゾンAmazonでAllegro ACS758電流センサーを購入するamzn.to
-
アマゾンAmazonでのACS758電流センサーamzn.to
-
アマゾンAmazonカナダのACS758電流センサーamzn.to
-
イーベイeBayからAllegro ACS758電流センサーを購入ebay.us
-
アリエクスプレスAliExpressでAllegro ACS758電流センサーを購入するs.click.aliexpress.com
リソースと参考文献
まだリソースはありません。
ファイル📁
他のファイル
-
Adafruit PCA9685 16チャネルサーボドライバ
robojax_PCA9685_extra_learning.pdf






























