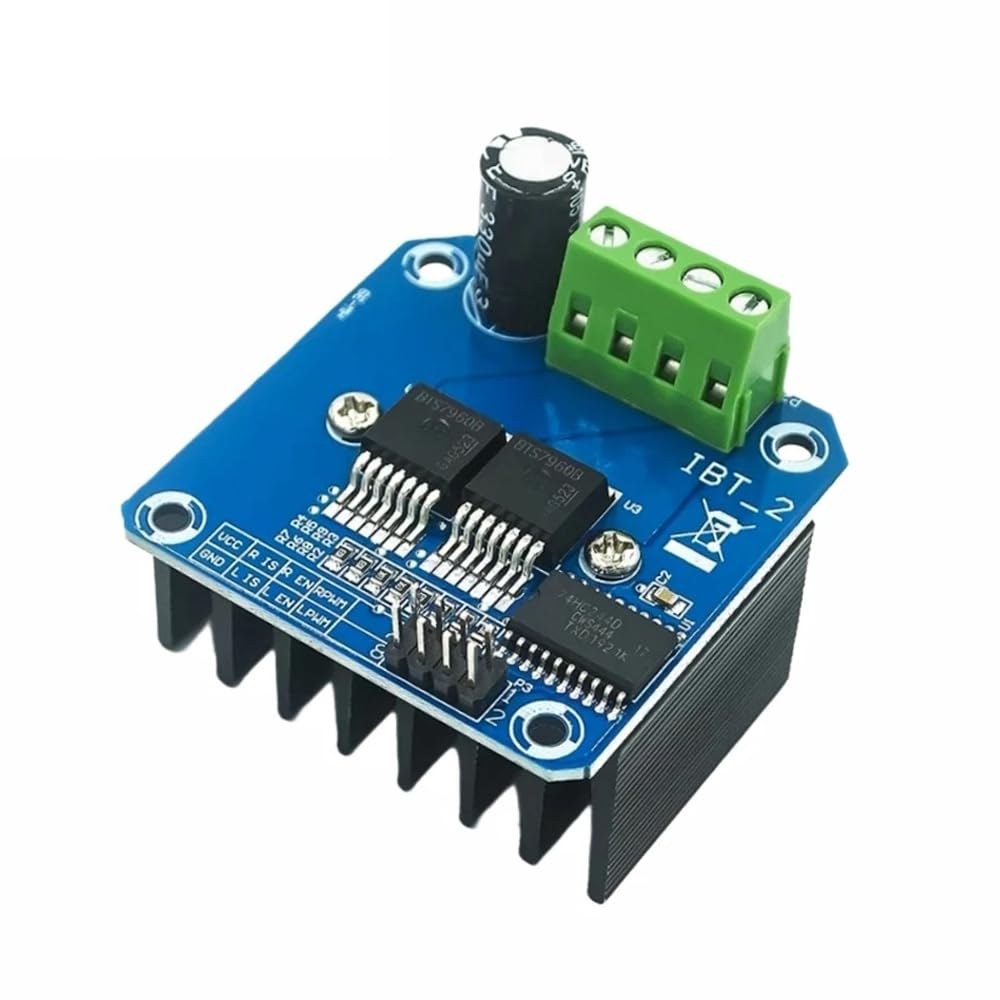
Controlling a BTS7960 DC Motor Driver Module with an Arduino
In this tutorial, we will learn how to control a BTS7960 DC motor driver module using an Arduino. This setup allows you to control a DC motor's direction and speed using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a working motor control system that you can easily modify for your own projects. For detailed visual guidance, make sure to check out the video at (in video at 00:00).
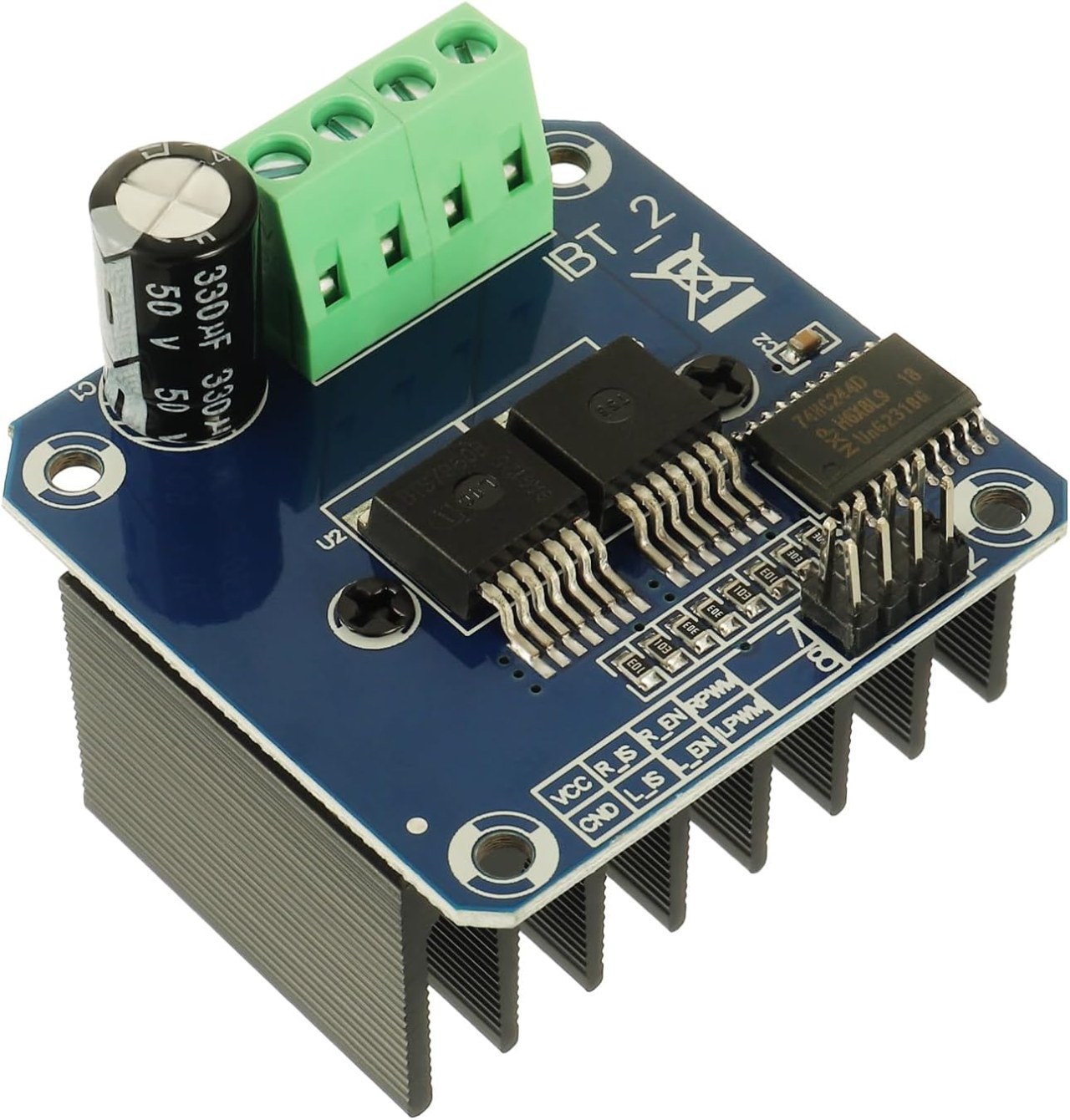
Hardware Explained
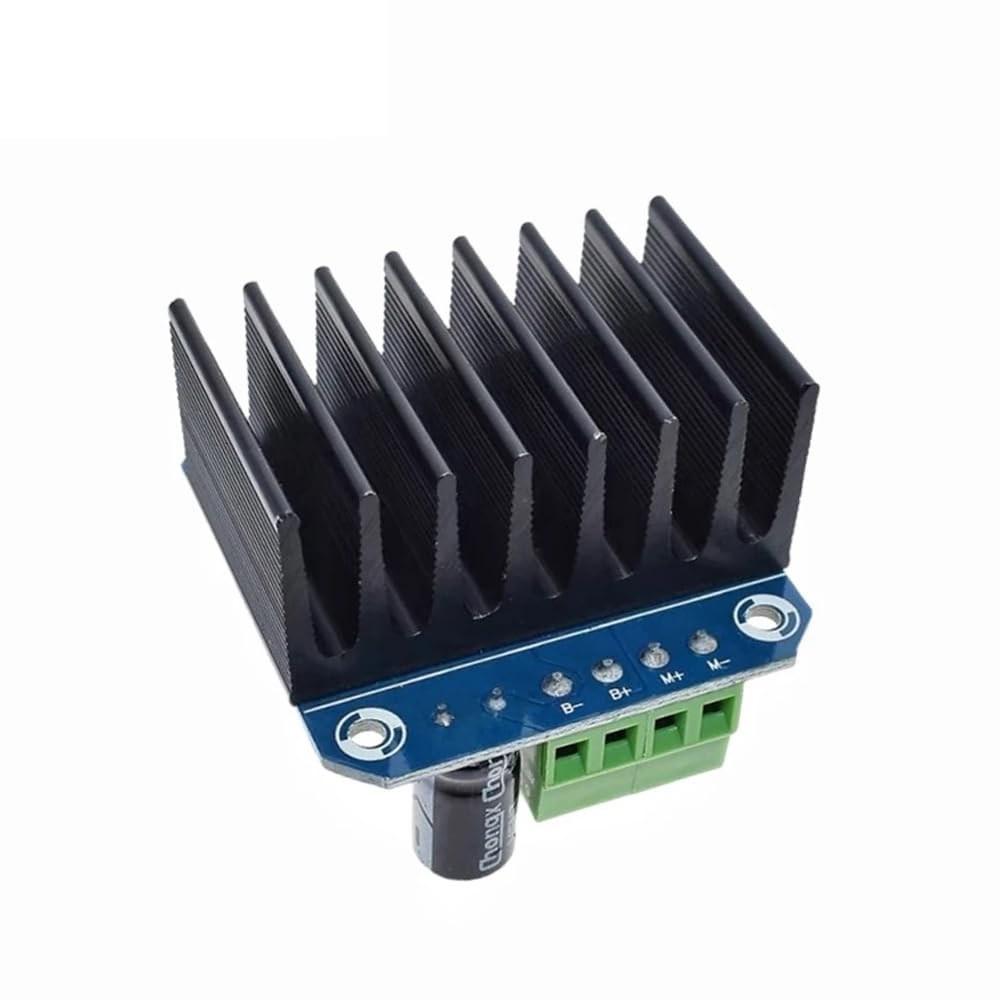
The BTS7960 is a high-current DC motor driver capable of handling up to 43 Amps. It consists of two integrated circuits (ICs) that allow control of a motor in both clockwise (CW) and counterclockwise (CCW) directions. The driver uses PWM signals to vary the speed of the motor, which is essential for applications requiring precise control.
Another important aspect of this module is its built-in current sensing and over-temperature protection features. This helps prevent damage to the motor and driver during operation. The module is powered from an external source, and it also requires a separate 5V supply for its logic circuits.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | Infineon Technologies |
|---|---|
| Part number | BTS7960 |
| Logic/IO voltage | 5 V |
| Supply voltage | 6–27 V |
| Output current (per channel) | 43 A max |
| Peak current (per channel) | 60 A |
| PWM frequency guidance | 25 kHz |
| Input logic thresholds | 0.8 V (high), 0.3 V (low) |
| Voltage drop / RDS(on) / saturation | 16 mΩ |
| Thermal limits | 125 °C max |
| Package | PTO-263-7 |
| Notes / variants | Dual H-Bridge configuration |
- Ensure proper heat sinking for high-current applications.
- Use appropriate wire gauge to handle the maximum current.
- Keep PWM frequency within specified limits for optimal performance.
- Implement decoupling capacitors near power pins to stabilize voltage.
- Monitor temperature during operation to prevent overheating.
Wiring Instructions
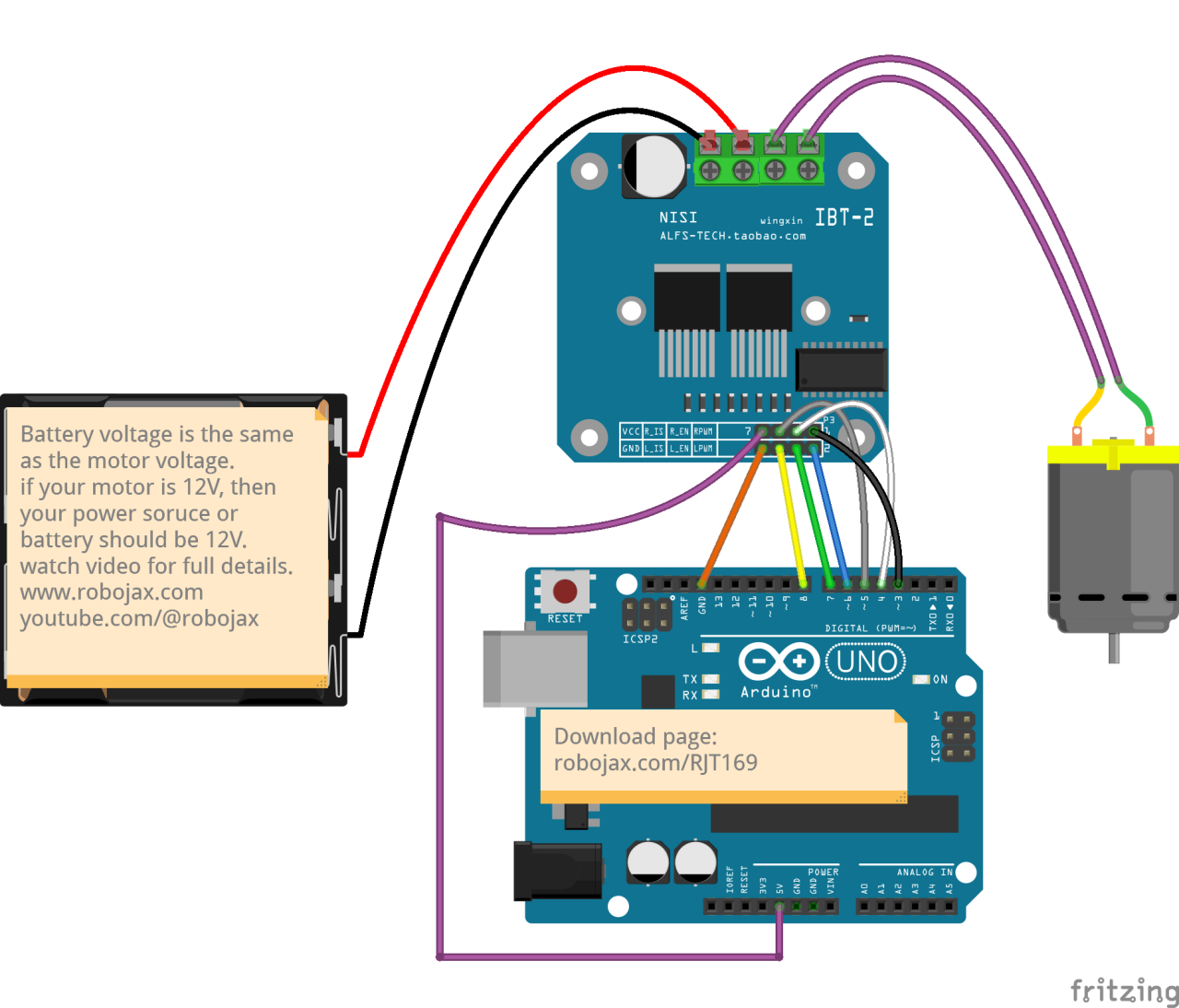
To wire the BTS7960 motor driver module to your Arduino, you'll need to connect the power, ground, control, and motor terminals correctly. Start by connecting the power supply to the module's B+ and B- terminals, ensuring the polarity is correct. The B+ terminal is where the positive supply connects, while B- connects to ground.
Next, connect the motor to the M+ and M- terminals on the module. These will control the direction of the motor. For control pins, connect the Arduino pins to the module as follows: RPWM to pin 3, R_EN to pin 4, R_IS to pin 5, LPWM to pin 6, L_EN to pin 7, and L_IS to pin 8. Make sure to connect the Arduino ground to the module ground as well.
Install required library
To install the robojax_BTS7960_motor_driver_library in the Arduino IDE, first download the library's ZIP file from the provided link. With the file saved, open your Arduino IDE and navigate to Sketch > Include Library > Add .ZIP Library.... In the file selection dialog, browse to the downloaded ZIP file, select it, and click "Open". The IDE will then install the library. You can confirm a successful installation by checking the File > Examples menu, where a new category named "Robojax BTS7960 Motor Driver Library" should appear. You can now include the library header in your code with #include <RobojaxBTS7960.h>.
Code Examples & Walkthrough
The Arduino code for controlling the BTS7960 motor driver begins with defining the necessary pins. For instance, the pin for the right PWM signal is defined as RPWM and set to pin 3. Additionally, the enable pin for the right side is defined as R_EN and set to pin 4.
#define RPWM 3 // define pin 3 for RPWM pin (output)
#define R_EN 4 // define pin 4 for R_EN pin (input)This setup ensures that the motor can be controlled accurately. In the setup() function, the motor is initialized with motor.begin(), which prepares the driver for operation.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);// setup Serial Monitor to display information
motor.begin(); // Initialize motor
}In the loop() function, the motor's direction and speed are controlled using the motor.rotate(speed, direction) method. For example, to run the motor at full speed clockwise, you would use motor.rotate(100, CW);.
void loop() {
motor.rotate(100,CW); // run motor with 100% speed in CW direction
delay(5000); // run for 5 seconds
}For more detailed examples and variations, be sure to check the full code loaded below the article.
Demonstration / What to Expect
When everything is wired and programmed correctly, you should expect the motor to rotate in both directions based on the code. Initially, the motor will run at full speed for five seconds, stop for three seconds, and then rotate in the opposite direction for the same duration. This cycle will repeat, allowing you to see the motor's responsiveness to the PWM signals.
Common pitfalls include reversed polarity when connecting the motor or power supply, which can damage the components. Additionally, ensure that the PWM pins are correctly assigned in the code (in video at 12:34).
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 Start
- 00:48 Hardware Explained
- 04:06 Datasheet viewed
- 07:07 Wiring Explained
- 09:00 Code explained
- 14:33 Demonstration
- 16:47 Maximum current test
- 19:25 Thermal image
- 19:27 Different code test
/*
* This is the Arduino code for the BTS7960 DC motor driver.
Using this code, you can control a motor to rotate in both directions: clockwise (CW)
and counter-clockwise (CCW).
Watch the video instructions: https://youtu.be/PUL5DZ9TA2o
📚⬇️ Download and resource page for this video https://robojax.com/RJT169
📚⬇️ Download and resource page https://robojax.com/RJT170
// Written by Ahmad Shamshiri for Robojax.com on
// June 22, 2019 at 14:08 in Ajax, Ontario, Canada.
Get this code and other Arduino codes from Robojax.com.
* BTS7960B
* Code is available at http://robojax.com/learn/arduino
* This code is "AS IS" without warranty or liability. Free to be used as long as you keep this note intact.
* This code has been downloaded from Robojax.com
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
//
#define RPWM 3 // define pin 3 for RPWM pin (output)
#define R_EN 4 // define pin 2 for R_EN pin (input)
#define R_IS 5 // define pin 5 for R_IS pin (output)
#define LPWM 6 // define pin 6 for LPWM pin (output)
#define L_EN 7 // define pin 7 for L_EN pin (input)
#define L_IS 8 // define pin 8 for L_IS pin (output)
#define CW 1 //do not change
#define CCW 0 //do not change
#define debug 1 //change to 0 to hide serial monitor debugging information or set to 1 to view
#include <RobojaxBTS7960.h>
RobojaxBTS7960 motor(R_EN,RPWM,R_IS, L_EN,LPWM,L_IS,debug);
void setup() {
// BTS7960 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
Serial.begin(9600);// setup Serial Monitor to display information
motor.begin();
//watch video for details: https://youtu.be/PUL5DZ9TA2o
// BTS7960 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
}
void loop() {
// BTS7960 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
//watch video for details: https://youtu.be/PUL5DZ9TA2o
motor.rotate(100,CW);// run motor with 100% speed in CW direction
delay(5000);//run for 5 seconds
motor.stop();// stop the motor
delay(3000);// stop for 3 seconds
motor.rotate(100,CCW);// run motor at 100% speed in CCW direction
delay(5000);// run for 5 seconds
motor.stop();// stop the motor
delay(3000); // stop for 3 seconds
// slowly speed up the motor from 0 to 100% speed
for(int i=0; i<=100; i++){
motor.rotate(i,CCW);
delay(50);
}
// slow down the motor from 100% to 0 with
for(int i=100; i>0; i--){
motor.rotate(i,CCW);
delay(50);
}
//watch video for details: https://youtu.be/PUL5DZ9TA2o
motor.stop();// stop motor
delay(3000); // stop for 3 seconds
// BTS7960 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
}// loop ends++
/*
* This is the Arduino code for the BTS7960 DC motor driver.
Using this code, you can control more than one motor to rotate in both directions: clockwise (CW)
and counter-clockwise (CCW).
📚⬇️ Download and resource page for this video https://robojax.com/RJT169
📚⬇️ Download and resource page https://robojax.com/RJT170
Written by Ahmad Shamshiri for Robojax.com on
July 16, 2020 in Ajax, Ontario, Canada.
Watch video instructions for this code: https://youtu.be/PUL5DZ9TA2o
BTS7960B
If you found this tutorial helpful, please support me so I can continue creating
content like this. You can support me on Patreon: http://robojax.com/L/?id=63
or make a donation using PayPal: http://robojax.com/L/?id=64
* This code has been downloaded from Robojax.com
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
// pins for motor 1
#define RPWM_1 3 // define pin 3 for RPWM pin (output)
#define R_EN_1 4 // define pin 2 for R_EN pin (input)
#define R_IS_1 5 // define pin 5 for R_IS pin (output)
#define LPWM_1 6 // define pin 6 for LPWM pin (output)
#define L_EN_1 7 // define pin 7 for L_EN pin (input)
#define L_IS_1 8 // define pin 8 for L_IS pin (output)
// motor 1 pins end here
// pins for motor 2
#define RPWM_2 9 // define pin 9 for RPWM pin (output)
#define R_EN_2 10 // define pin 10 for R_EN pin (input)
#define R_IS_2 12 // define pin 12 for R_IS pin (output)
#define LPWM_2 11 // define pin 11 for LPWM pin (output)
#define L_EN_2 A0 // define pin 7 for L_EN pin (input)
#define L_IS_2 A1 // define pin 8 for L_IS pin (output)
// motor 2 pins end here
#define CW 1 //
#define CCW 0 //
#define debug 1 //
#include <RobojaxBTS7960.h>
RobojaxBTS7960 motor1(R_EN_1,RPWM_1,R_IS_1, L_EN_1,LPWM_1,L_IS_1,debug);//define motor 1 object
RobojaxBTS7960 motor2(R_EN_2,RPWM_2,R_IS_2, L_EN_2,LPWM_2,L_IS_2,debug);//define motor 2 object and the same way for other motors
void setup() {
// BTS7960 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
Serial.begin(9600);// setup Serial Monitor to display information
motor1.begin();
motor2.begin();
// BTS7960 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
}
void loop() {
// BTS7960 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
motor1.rotate(100,CW);// run motor 1 with 100% speed in CW direction
delay(5000);//run for 5 seconds
motor1.stop();// stop the motor 1
delay(3000);// stop for 3 seconds
motor1.rotate(100,CCW);// run motor 1 at 100% speed in CCW direction
delay(5000);// run for 5 seconds
motor1.stop();// stop the motor 1
delay(3000); // stop for 3 seconds
motor2.rotate(100,CW);// run motor 2 with 100% speed in CW direction
delay(5000);//run for 5 seconds
motor2.stop();// stop the motor 2
delay(3000);// stop for 3 seconds
motor2.rotate(100,CCW);// run motor 2 at 100% speed in CCW direction
delay(5000);// run for 5 seconds
motor2.stop();// stop the motor 2
delay(3000); // stop for 3 seconds
// slowly speed up the motor 1 from 0 to 100% speed
for(int i=0; i<=100; i++){
motor1.rotate(i,CCW);
delay(50);
}
// slow down the motor 2 from 100% to 0
for(int i=100; i>0; i--){
motor2.rotate(i,CCW);
delay(50);
}
motor2.stop();// stop motor 2
delay(3000); // stop for 3 seconds
// BTS7960 more than 1 Motor Control Code by Robojax.com 20190622
}// loop endsРесурсы и ссылки
-
ВнешнийBTS7960 Амазон Японияamzn.to
-
ВнешнийBTS7960 на Amazon Italiaamzn.to
-
ВнешнийBTS7960 на Amazon Испанияamzn.to
-
ВнешнийBTS7960 на Amazon Францияamzn.to
-
ВнешнийBTS7960, Amazon Германияamzn.to
-
ВнешнийКупите BTS7960 на Amazonamzn.to
-
ВнешнийКупите BTS7960 на Amazon Канадаamzn.to
-
ВнешнийКупить BTS7960, Amazon UKamzn.to
Файлы📁
Библиотеки Arduino (zip)
-
robojax_BTS7960_библиотека_управления_мотором
robojax_BTS7960_motor_driver_library.zip0.10 MB
Технический паспорт (pdf)
-
BTS7960_datasheet
BTS7960_datasheet.pdf0.45 MB
Файл Fritzing
-
BTS7960_драйвер
BTS7960_driver.fzpz0.01 MB