Come utilizzare un Arduino come telecomando per TV
Questa guida dimostra come trasformare un Arduino in un telecomando universale per il tuo televisore, lettore Blu-ray o altri dispositivi controllati a infrarossi. Imparerai a decodificare i segnali da qualsiasi telecomando, quindi trasmettere quei codici utilizzando un Arduino e un LED a infrarossi. Questo apre un mondo di possibilità di automazione, da un semplice controllo on/off a sequenze complesse che coinvolgono più dispositivi.

Ecco alcune idee per progetti per iniziare:
- Crea un sistema di accensione/spegnimento programmato per la TV.
- Integra il controllo della tua TV in un sistema di casa intelligente.
- Crea un telecomando personalizzato con funzioni uniche.
- Controlla il tuo sistema di intrattenimento con comandi vocali tramite un assistente vocale basato su Arduino.
Hardware/Componenti
- Arduino Uno (o scheda compatibile)
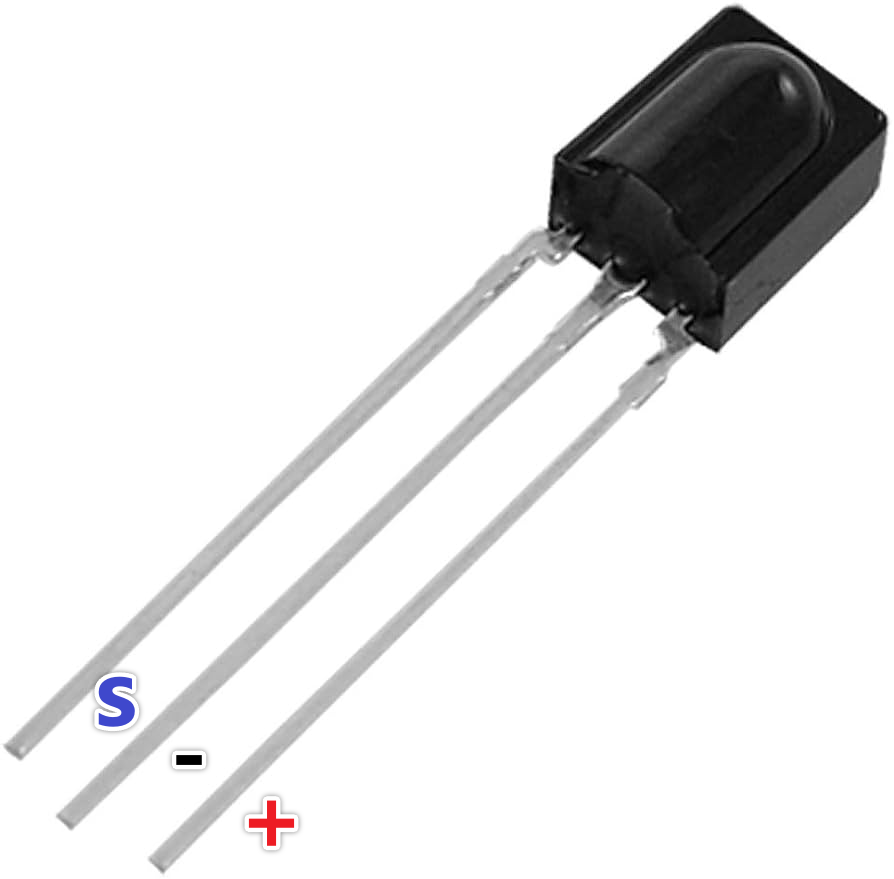
- Modulo ricevitore a infrarossi (IR) (ad es., TSOP1738, VS1838B)
- LED a infrarossi (IR) (ad es., lunghezza d'onda di 940 nm)
- Resistore (270-330 ohm per il LED IR)
- Cavi jumper
- Piastra di prototipazione (opzionale)
Guida al cablaggio

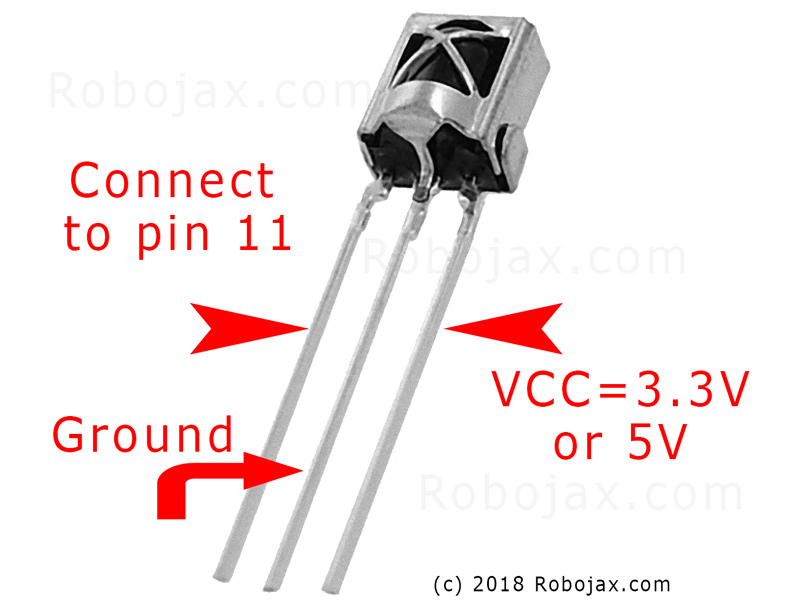
Collegare il modulo del ricevitore IR come segue (nel video al 02:45):
- VCC a Arduino 5V
- GND a GND di Arduino
- Pinn signal al pin 11 di Arduino (può essere cambiato nel codice)
Collegare il LED IR come segue (nel video al minuto 02:07):
- Un pin LED al pin 3 dell'Arduino (attraverso una resistenza da 270-330 ohm)
- Altro pin LED a GND di Arduino
Il resistore limita la corrente all'LED IR, proteggendolo dai danni (nel video al 03:37).
Spiegazione del codice
Prima di tutto, installa la libreria IRremote (nel video a 04:16). Questa libreria gestisce le complessità dell'invio e della ricezione di segnali infrarossi. Puoi trovarla nel Gestore delle librerie di Arduino.
I frammenti di codice forniti sono a scopo di riferimento. La libreria IRremote include codice di esempio per ricevere e inviare segnali IR. Gli esempi possono essere trovati nell'IDE di Arduino: File > Esempi > IRremote.
Codice di Ricezione
Questo frammento di codice configura il ricevitore sul pin 11 (nel video alle 04:50). Modifica ilRECV_PINse stai usando un PIN diverso.
#include
int RECV_PIN = 11;
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
decode_results results;
Invio del codice
Questo codice invia il codice IR grezzo catturato. Ilrawl'array memorizza i tempi del segnale, e38rappresenta la frequenza (in kHz). Dovrai sostituire i dati di esempio con il codice catturato dal tuo telecomando (nel video al 05:26).
irsend.sendRaw(raw, sizeof(raw) / sizeof(raw[0]), 38);
Ilsizeof(raw) / sizeof(raw[0])calcola il numero di elementi nelrawarray (nel video alle 06:18).
Progetto dal vivo/Demonstrazione
Il video dimostra come catturare il codice del pulsante di accensione da un telecomando Samsung TV e quindi utilizzare l'Arduino per accendere e spegnere la TV (nel video alle 08:29). Il processo prevede la cattura del codice utilizzando lo sketch di ricezione, per poi incollare quel codice nello sketch di invio. La dimostrazione mostra come l'Arduino riesca a imitare con successo il telecomando originale.
Capitoli
- [00:00] Introduzione e Panoramica del Progetto
- [00:41] Comprendere il telecomando a infrarossi
- [02:07] Componenti hardware e cablaggio
- [04:16] Installazione della libreria IRremote
- [05:26] Inviare segnali IR con Arduino
- [06:46] Testare la trasmissione IR
- [08:29] Dimostrazione dal vivo con un televisore Samsung
- [09:27] Espandere il Progetto e Ulteriori Idee
#include <IRremote.h>
// Sketch from:
//https://gist.github.com/probonopd/5793692#file-sendandreceive-ino
// http://www.pjrc.com/teensy/td_libs_IRremote.html
// If one keypress results in multiple codes being output, then
// change in IRremoteInt.h:
// #define _GAP 50000
// Provided by Robojax.com on August 4, 2018
// Watch video instructions for this code:https://youtu.be/xA66hXYRx9I
int RECV_PIN = 11;
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
decode_results results;
// Compare two tick values, returning 0 if newval is shorter,
// 1 if newval is equal, and 2 if newval is longer.
// Use a tolerance of 20%
int compare(unsigned int oldval, unsigned int newval) {
if (newval < oldval * .8) {
return 0;
}
else if (oldval < newval * .8) {
return 2;
}
else {
return 1;
}
}
// Use FNV hash algorithm: http://isthe.com/chongo/tech/comp/fnv/#FNV-param
#define FNV_PRIME_32 16777619
#define FNV_BASIS_32 2166136261
/* Converts the raw code values into a 32-bit hash code.
* Hopefully this code is unique for each button.
*/
unsigned long decodeHash(decode_results *results) {
unsigned long hash = FNV_BASIS_32;
for (int i = 1; i+2 < results->rawlen; i++) {
int value = compare(results->rawbuf[i], results->rawbuf[i+2]);
// Add value into the hash
hash = (hash * FNV_PRIME_32) ^ value;
}
return hash;
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Robojax IR Capture");
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the receiver
}
int c = 1;
void dump(decode_results *results) {
int count = results->rawlen;
Serial.println(c);
c++;
Serial.println("Hash: ");
unsigned long hash = decodeHash(results);
Serial.println(hash, HEX);
Serial.println("For IR Scope/IrScrutinizer: ");
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
if ((i % 2) == 1) {
Serial.print("+");
Serial.print(results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
else {
Serial.print(-(int)results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println("-127976");
Serial.println("For Arduino sketch: ");
Serial.print("unsigned int raw[");
Serial.print(count, DEC);
Serial.print("] = {");
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
if ((i % 2) == 1) {
Serial.print(results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
else {
Serial.print((int)results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
Serial.print(",");
}
Serial.print("};");
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("irsend.sendRaw(raw,");
Serial.print(count, DEC);
Serial.print(",38);");
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("");
}
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <avr/pgmspace.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <avr/io.h>
#define IR_PORT PORTB
// #define IR_PIN PINB
// #define IR_DDR DDRB
// #define IR_BV _BV(1)
#define IR_OCR OCR1A
#define IR_TCCRnA TCCR1A
#define IR_TCCRnB TCCR1B
#define IR_TCNTn TCNT1
#define IR_TIFRn TIFR1
#define IR_TIMSKn TIMSK1
#define IR_TOIEn TOIE1
#define IR_ICRn ICR1
#define IR_OCRn OCR1A
#define IR_COMn0 COM1A0
#define IR_COMn1 COM1A1
#define PRONTO_IR_SOURCE 0 // Pronto code byte 0
#define PRONTO_FREQ_CODE 1 // Pronto code byte 1
#define PRONTO_SEQUENCE1_LENGTH 2 // Pronto code byte 2
#define PRONTO_SEQUENCE2_LENGTH 3 // Pronto code byte 3
#define PRONTO_CODE_START 4 // Pronto code byte 4
static const uint16_t *ir_code = NULL;
static uint16_t ir_cycle_count = 0;
static uint32_t ir_total_cycle_count = 0;
static uint8_t ir_seq_index = 0;
static uint8_t ir_led_state = 0;
void ir_on()
{
IR_TCCRnA |= (1<<IR_COMn1) + (1<<IR_COMn0);
ir_led_state = 1;
}
void ir_off()
{
IR_TCCRnA &= ((~(1<<IR_COMn1)) & (~(1<<IR_COMn0)) );
ir_led_state = 0;
}
void ir_toggle()
{
if (ir_led_state)
ir_off();
else
ir_on();
}
void ir_start(uint16_t *code)
{
ir_code = code;
// IR_PORT &= ~IR_BV; // Turn output off (atmega328 only)
digitalWrite(9,LOW); // Turn output off
// IR_DDR |= IR_BV; // Set it as output (atmega328 only)
pinMode(9,OUTPUT); // Set it as output
IR_TCCRnA = 0x00; // Reset the pwm
IR_TCCRnB = 0x00;
//printf_P(PSTR("FREQ CODE: %hd\r\n"), code[PRONTO_FREQ_CODE]);
uint16_t top = ( (F_CPU/1000000.0) * code[PRONTO_FREQ_CODE] * 0.241246 ) - 1;
//printf_P(PSTR("top: %hu\n\r"), top);
IR_ICRn = top;
IR_OCRn = top >> 1;
IR_TCCRnA = (1<<WGM11);
IR_TCCRnB = (1<<WGM13) | (1<<WGM12);
IR_TCNTn = 0x0000;
IR_TIFRn = 0x00;
IR_TIMSKn = 1 << IR_TOIEn;
ir_seq_index = PRONTO_CODE_START;
ir_cycle_count = 0;
ir_on();
IR_TCCRnB |= (1<<CS10);
}
#define TOTAL_CYCLES 80000 // Turns off after this number of
// cycles. About 2 seconds.
// FIXME: Turn off after having sent all data
ISR(TIMER1_OVF_vect) {
uint16_t sequenceIndexEnd;
uint16_t repeatSequenceIndexStart;
ir_total_cycle_count++;
ir_cycle_count++;
if (ir_cycle_count== ir_code[ir_seq_index]) {
ir_toggle();
ir_cycle_count = 0;
ir_seq_index++;
sequenceIndexEnd = PRONTO_CODE_START +
(ir_code[PRONTO_SEQUENCE1_LENGTH]<<1) +
(ir_code[PRONTO_SEQUENCE2_LENGTH]<<1);
repeatSequenceIndexStart = PRONTO_CODE_START +
(ir_code[PRONTO_SEQUENCE1_LENGTH]<<1);
if (ir_seq_index >= sequenceIndexEnd ) {
ir_seq_index = repeatSequenceIndexStart;
if(ir_total_cycle_count>TOTAL_CYCLES) {
ir_off();
TCCR1B &= ~(1<<CS10);
}
}
}
}
void ir_stop()
{
IR_TCCRnA = 0x00; // Reset the pwm
IR_TCCRnB = 0x00;
}
const uint16_t inputLength = 512;
void loop() {
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) {
dump(&results);
irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value
}
if ( Serial.available() > 0 )
{
static char input[inputLength];
static uint16_t i;
char c = Serial.read();
if ( c != '\r' && c != '\n' && i < inputLength-1)
input[i++] = c;
else
{
input[i] = '\0';
i = 0;
uint16_t array[80];
uint16_t j = 0;
if ( !strncmp(input, "SEND", 4) )
{
char* p = input+4;
while ( (p = strchr(p, ' ')) != NULL )
array[j++] = strtol(p, &p, 16);
ir_start(array);
Serial.print("SENT ");
for ( uint8_t i = 0; i < j; i++ )
{
Serial.print ("0x");
Serial.print (array[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
}
}
}
}Cose di cui potresti avere bisogno
-
Amazon
-
eBay
Risorse e riferimenti
-
Esterno
File📁
Nessun file disponibile.