用Arduino解码黑色或白色遥控器
在本教程中,我们将学习如何使用Arduino和红外接收器解码黑白红外遥控器的按键。在本项目结束时,您将能够确定遥控器上按下了哪个按键,并将该信息显示在串口监视器上。这对于控制您可能拥有的任何遥控设备(例如电视或其他电器)非常有用(视频时间:01:00)。

我们将使用一个简单的设置,包括一个Arduino、一个红外接收模块和必要的解码代码。红外接收器将捕获遥控器发送的信号,Arduino将解读这些信号以确定哪个按钮被按下。这个项目很简单,并可以适应各种遥控器。

硬件解释
该项目的主要组件包括Arduino开发板和一个红外接收模块,通常标记为VS1838B。Arduino将作为主控制器,执行处理来自遥控器信号的代码。红外接收器捕捉遥控器发出的红外信号,并将其转换为Arduino可以理解的格式。
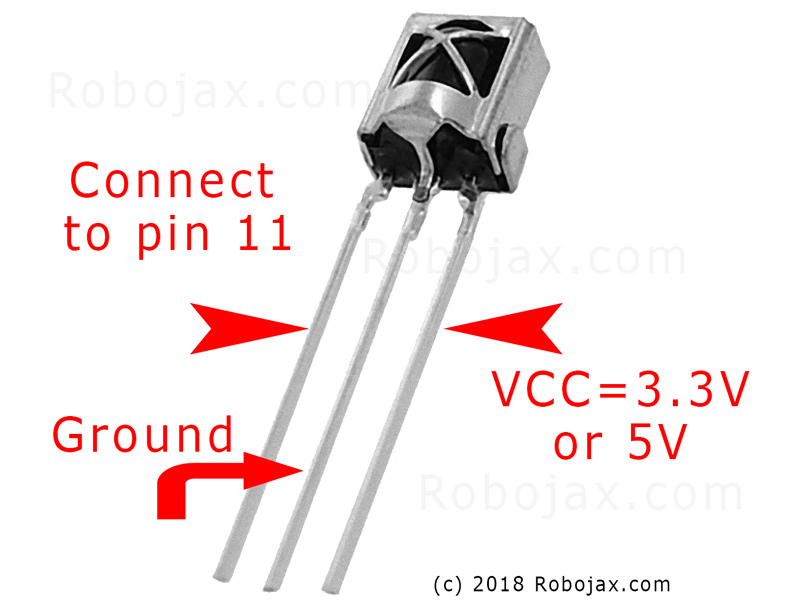
VS1838B的工作电压范围为2.7V至5.5V,使其与大多数Arduino开发板兼容。它可以在10到15米的距离内检测信号,具体取决于环境条件。红外接收器输出一个数字信号,指示遥控器上哪个按钮被按下,从而使Arduino能够做出相应的响应。
数据表详细信息
| 生产厂家 | VS1838B |
|---|---|
| 零件编号 | VS1838B |
| 逻辑/IO电压 | 2.7-5.5 伏 |
| 供电电压 | 5 V |
| 输出电流(每通道) | 1.5 毫安 |
| 接收距离 | 10-15米 |
| 输入频率 | 38 kHz |
| 静态电流 | 0.8 毫安(典型值) |
| 操作角度 | 70度 |
| 包裹 | TO-220 |
- 确保提供适当的电压以避免损坏红外接收器。
- 请将接收模块远离直接阳光或强红外源。
- 如有必要,请使用上拉电阻以稳定信号读数。
- 接线连接应牢固,以防止信号间歇性。
- 测试不同的遥控器,以查看它们与系统的兼容性。
-

解码红外遥控器主控-1
接线说明
要将红外接收器连接到Arduino,首先将红外接收器的VCC引脚连接到Arduino的5V引脚。接下来,将接收器的GND引脚连接到Arduino的一个GND引脚。最后,将红外接收器的信号引脚(通常标记为SIG或OUT)连接到Arduino的数字引脚11。
确保连接牢固,因为松动的连接可能导致读数不一致。如果您使用的是红外接收器的PCB版本或裸模块,接线保持不变;只需根据模块的标签正确识别引脚即可(视频中在03:15)。
安装IRremote库
启动 Arduino IDE。Arduino.cc免费) 点击左侧的图书馆图标并搜索IRremote点击“安装”以进行安装。
#include <IRremote.h>代码示例与演练
int RECV_PIN = 11;
const char type ='W'; // W for white, B for black
const boolean PCB = 0; // 1 for PCB, 0 for bare module
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);在这一段中,我们为红外接收器定义引脚编号。RECV_PIN设置为11。我们还指定所使用的遥控器类型。type变量,其中 'W' 表示白色遥控器,'B' 表示黑色遥控器。PCB变量区分使用接收器的PCB版本或裸模块。
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the receiver
}在setup()我们以9600波特率初始化串行通信并启动红外接收器。这对于监控串行监视器上的输出至关重要,使我们能够看到哪个键被按下。
void loop() {
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) {
robojaxValidateCode(results.value); // Validate the received code
irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value
}
delay(100);
}主要loop()检查红外接收器是否已解码信号。如果已解码,则调用robojaxValidateCode处理接收到的值的函数,然后恢复监听下一个信号。delay(100)确保循环不会运行得太快,这有助于信号处理。
演示 / 期待什么
一切设置好并且代码上传后,打开串口监视器查看输出。当您按下遥控器上的一个按键时,您应该会在监视器上看到相应的按键名称。如果按键未被识别,它将显示“按键未知”。确保按键稳固按下,因为松动的连接可能会导致错误的读数(在视频的 05:40)。
如果您持续按下一个键,输出可能会显示重复的值或十六进制代码。这种行为是正常的,您可以修改代码以过滤掉这些连续信号(如果需要)。此外,您可以调整代码以根据特定的按键操作执行动作,例如打开灯光或控制其他设备。
视频时间戳
- 00:00 开始
- 硬件的解释
- 04:26 电线连接说明
- 05:20 代码已解释
- 12:27 代码解码演示
/*
* Original code and library from - http://arcfn.com
*
* This code decodes keys of Black IR remote and White IR remote
* sold on eBay for Arduino.
* You have to select the type of your remote as Black or White in the code below
* and also select your receiver 1838 either as PCB or bare module. See video for details
*
* Modified/Written by Ahmad Shamshiri
* on July 28, 2018 at 22:48 in Ajax, Ontario, Canada
* for Robojax.com
* Watch video instruction for this code:https://youtu.be/muAkBQb24NI
* Get other Arduino codes from Robojax.com
*
*/
#include <IRremote.h>
int RECV_PIN = 11;
const char type ='W';// W for white, B for black. Must keep single quotes like 'B' or 'W'
const boolean PCB = 0;// if receiver is PCB set to 1, if not set to 0. See video for details
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
// this is array holding codes for White Remote when used with PCB version of receiver
unsigned int whiteRemotePCB[] ={
0xE318261B, // CH-
0x511DBB, // CH
0xEE886D7F, // CH+
0x52A3D41F, // |<<
0xD7E84B1B, // >>|
0x20FE4DBB, // >||
0xF076C13B, // -
0xA3C8EDDB, // +
0x12CEA6E6, // EQ
0xC101E57B, // 0
0x97483BFB, // 100+
0xF0C41643, // 200+
0x9716BE3F, // 1
0x3D9AE3F7, // 2
0x6182021B, // 3
0x8C22657B, // 4
0x488F3CBB, // 5
0x449E79F, // 6
0x32C6FDF7, // 7
0x1BC0157B, // 8
0x3EC3FC1B // 9
};
// this is array holding codes for White Remote when used with non-PCB version of receiver
unsigned int whiteRemote[] ={
0xFFA25D, // CH-
0xFF629D, // CH
0xFFE21D, // CH+
0xFF22DD, // |<<
0xFF02FD, // >>|
0xFFC23D, // >||
0xFFE01F, // -
0xFFA857, // +
0xFF906F, // EQ
0xFF6897, // 0
0xFF9867, // 100+
0xFFB04F, // 200+
0xFF30CF, // 1
0xFF18E7, // 2
0xFF7A85, // 3
0xFF10EF, // 4
0xFF38C7, // 5
0xFF5AA5, // 6
0xFF42BD, // 7
0xFF4AB5, // 8
0xFF52AD // 9
};
// key labels of white remote
String whiteRemoteKey[] ={
"CH-",
"CH",
"CH+",
"|<<",
">>|",
">||",
"-",
"+",
"EQ",
"0",
"100+",
"200+",
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"5",
"6",
"7",
"8",
"9"
};
// this is array holding codes for Black Remote when used with non-PCB version of receiver
unsigned int blackRemote[] ={
0xFF629D, // ^
0xFF22DD, // <
0xFF02FD, // OK
0xFFC23D, // >
0xFFA857, // v
0xFF6897, // 1
0xFF9867, // 2
0xF0C41643, // 3
0xFF30CF, // 4
0xFF18E7, // 5
0xFF7A85, // 6
0xFF10EF, // 7
0xFF38C7, // 8
0xFF5AA5, // 9
0xFF42BD, // *
0xFF4AB5, // 0
0xFF52AD // #
};
// this is array holding codes for Black Remote when used with PCB version of receiver
unsigned int blackRemotePCB[] ={
0x511DBB, // ^
0x52A3D41F, // <
0xD7E84B1B, // OK
0x20FE4DBB, // >
0xA3C8EDDB, // v
0xC101E57B, // 1
0x97483BFB, // 2
0xF0C41643, // 3
0x9716BE3F, // 4
0x3D9AE3F7, // 5
0x6182021B, // 6
0x8C22657B, // 7
0x488F3CBB, // 8
0x449E79F, // 9
0x32C6FDF7, // *
0x1BC0157B, // 0
0x3EC3FC1B // #
};
// Black remote key names
String blackRemoteKey[] ={
"^",
"<",
"OK",
">",
"v",
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"5",
"6",
"7",
"8",
"9",
"*",
"0",
"#"
};
decode_results results;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
// In case the interrupt driver crashes on setup, give a clue
// to the user what's going on.
Serial.println("Robojax Remote Decoder");
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the receiver
}
void loop() {
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) {
//Serial.println(results.value, HEX);
robojaxValidateCode(results.value);// used the "robojaxValidateCode" below
irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value
}
delay(100);
}
/*
* function: robojaxValidateCode
* validates the remote code and prints correct key name
* cd is code passed from the loop
* Written by A. S. for Robojax
*/
void robojaxValidateCode(int cd)
{
// Robojax IR Remote decoder
int found=0;
if(type =='W' && !PCB)
{
// Robojax IR White Remote decoder
// if type is set to 'W' (white remote) and PCB=0 then check Black remote code
for(int i=0; i< sizeof(whiteRemote)/sizeof(int); i++)
{
if(whiteRemote[i] ==cd)
{
Serial.print("Key pressed:");
Serial.println(whiteRemoteKey[i]);
found=1;
}// if matched
}// for
}else if(type =='W' && PCB){
// Robojax IR White Remote decoder
// if type is set to 'W' (white remote) and PCB=1 then check Black remote code
for(int i=0; i< sizeof(whiteRemotePCB)/sizeof(int); i++)
{
if(whiteRemotePCB[i] ==cd)
{
Serial.print("Key pressed:");
Serial.println(whiteRemoteKey[i]);
found=1;
}// if matched
}// for
}else if(type =='B' && PCB){
// Robojax IR White Remote decoder
// if type is set to 'B' (black remote) and PCB=1 then check Black remote code
for(int i=0; i< sizeof(blackRemotePCB)/sizeof(int); i++)
{
// Robojax IR black Remote decoder
if(blackRemotePCB[i] ==cd)
{
Serial.print("Key pressed:");
Serial.println(blackRemoteKey[i]);
found=1;
}// if matched
}// for
}else{
// if type is set to 'B' (black remote) and PCB =0 then check Black remote code
for(int i=0; i< sizeof(blackRemote)/sizeof(int); i++)
{
// Robojax IR black Remote decoder
if(blackRemote[i] ==cd)
{
if(blackRemoteKey[i] == "OK"){
digitalWrite(9,HIGH);
}
Serial.print("Key pressed:");
Serial.println(blackRemoteKey[i]);
found=1;
}// if matched
}// for
}// else
if(!found){
if(cd !=0xFFFFFFFF)
{
Serial.println("Key unknown");
}
}// found
}|||您可能需要的东西
-
亚马逊从亚马逊购买红外遥控器amzn.to
-
易趣从eBay购买红外遥控器ebay.us
资源与参考
尚无可用资源。
文件📁
没有可用的文件。