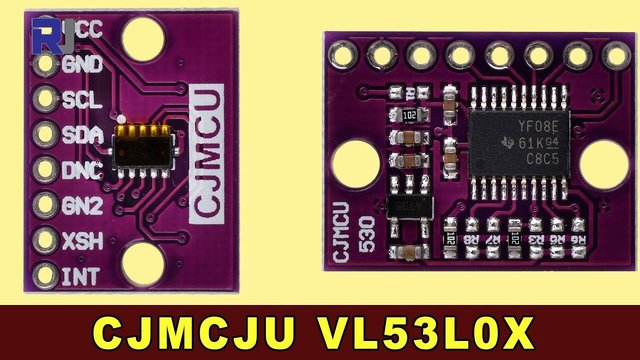
使用CJMCU VL53L0X激光测距仪与Arduino
本教程演示如何将CJMCU VL53L0X激光测距仪与Arduino结合使用。该模块配备了德州仪器的VL53L0X飞行时间传感器和TXS0108E双向电平转换器(视频中的00:06),可以实现高达两米的精确测距(视频中的00:52)。它与各种逻辑电平(3.3V、1.8V、5V)的兼容性简化了与不同微控制器的集成(视频中的00:21)。这个项目为广泛的可能性打开了大门。
项目创意:
- 机器人技术:在机器人中实现障碍物避让。
- 自动化:根据接近度控制机械。
- 智能家居:根据距离创建自动照明。
- 安全:开发一个基于距离的报警系统。
硬件/组件
要构建这个项目,您将需要以下组件:
- Arduino 板(任何型号均可使用)
- CJMCU VL53L0X 激光测距传感器模块
- 跳线
接线指南
VL53L0X 模块连接到 Arduino 如下:
将模块的VCC引脚连接到Arduino的5V引脚。模块内部的稳压器处理传感器所需的3.3V。(视频中的时间为01:50)
将模块的GND引脚连接到Arduino的GND引脚。
将模块的SDA引脚连接到Arduino的A4引脚。
将模块的SCL引脚连接到Arduino的A5引脚。
如果不需要使用 XSHUT 引脚进行关机控制,请保持其未连接。(在视频中为 03:50)
代码解释
提供的代码使用了 VL53L0X 库。以下是关键可配置部分的解释:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <VL53L0X.h>
VL53L0X sensor;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
// ... other setup code ...
sensor.setTimeout(500); // Set timeout to 500ms (in video at 06:40)
sensor.startContinuous(); // Start continuous measurement mode (in video at 06:50)
}
void loop()
{
Serial.print(sensor.readRangeContinuousMillimeters()); // Read distance in mm (in video at 07:01)
// ... other loop code ...
}
这个sensor.setTimeout(500)该行将距离测量的超时时间设置为500毫秒。如果您的应用程序需要,请根据需要调整此值(视频中见06:40)。sensor.startContinuous()函数启动连续测距,以尽可能快的速度提供距离读数(视频时间06:50)。sensor.readRangeContinuousMillimeters()函数返回以毫米为单位的测量距离(在视频中的时间为07:01)。
实时项目/演示
该视频演示了传感器的操作,显示了当传感器到目标的距离变化时,距离读数是如何变化的。读数在几毫米内是准确的,特别是在超过10毫米的距离(在视频中为08:20)。在非常近的范围内(小于10毫米),准确度会下降(在视频中为09:50)。演示还显示,反射表面可能会影响读数,尤其是在激光与表面不垂直的情况下(在视频中为10:32)。
章节
- [00:00] 介绍和项目概述
- [00:48] VL53L0X传感器详情
- 模块概述和规格
- [02:55] 应用程序和标准
- [03:35] 引脚定义和连接
- [05:29] 代码解释
- [07:45] 接线和连接
- [08:18] 现场演示
/* This example shows how to use continuous mode to take
range measurements with the VL53L0X. It is based on
vl53l0x_ContinuousRanging_Example.c from the VL53L0X API.
The range readings are in units of mm.
Updated by Ahmad Shamshiri for Robojax.com on July 23, 2018 in Ajax, Ontario, Canada.
Watch video instructions for this code: https://youtu.be/0PnAyt51IU4
Download the library and get other resources for this code at http://robojax.com
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <VL53L0X.h>
VL53L0X sensor;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Robojax CJMCU VL523L0X laser distance test");
Wire.begin();
sensor.init();
sensor.setTimeout(500);
// Start continuous back-to-back mode (take readings as
// fast as possible). To use continuous timed mode
// instead, provide a desired inter-measurement period in
// ms (e.g. sensor.startContinuous(100)).
sensor.startContinuous();
}
void loop()
{
Serial.print(sensor.readRangeContinuousMillimeters());// print distance
if (sensor.timeoutOccurred()) { Serial.print(" TIMEOUT"); }
Serial.println();
}资源与参考
-
外部Pololu 下载(GitHub)github.com
-
外部TXS0108E 数据表ti.com
文件📁
没有可用的文件。