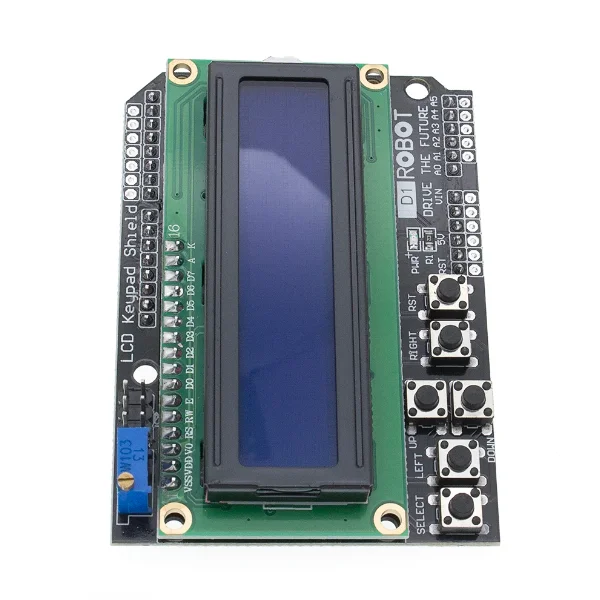
如何设置I²C地址并使用I²C扫描仪来操作LCD1602和LCD2004
在本教程中,我们将探索如何设置 I²C 地址以及如何为 LCD1602 和 LCD2004 显示器使用 I²C 扫描器。理解 I²C 通信对于将这些 LCD模块与您的 Arduino 项目集成至关重要,从而实现高效的数据传输和控制。在本指南结束时,您将能够有效识别 LCD 的 I²C 地址,并确保它们正常工作。


我们将在此项目中使用BMP-180传感器,它采用I²C通信。传感器提供温度和压力读数,可以显示在LCD1602或LCD2004上。本教程将包括接线说明、代码片段以及预期结果的演示。为了更直观的理解,请务必查看相关视频(视频在:00:00)。
硬件解析
该项目的主要组件包括BMP-180传感器、LCD1602或LCD2004显示屏和Arduino板。BMP-180是一种数字压力传感器,通过I²C协议进行通信,仅需两条数据线:SDA(数据线)和SCL(时钟线)。LCD显示屏也支持I²C,并可以使用相同的通信协议轻松控制,从而实现干净高效的设置。
BMP-180 的工作电压在 1.8V 至 3.6V 之间,这意味着如果您使用更高电压的电源,可以通过电压调节器为其供电。另一方面,LCD 显示器通常在 5V 下工作,这使得与 Arduino 板的接口变得容易,无需任何额外组件。
数据表详细信息
| 制造商 | 博世 |
|---|---|
| 部件编号 | BMP-180 |
| 逻辑/输入输出电压 | 1.8 - 3.6 伏 |
| 供电电压 | 1.8 - 3.6 V |
| 输出电流(每通道) | 3.6 微安培 |
| 峰值电流(每通道) | 1 毫安 |
| PWM频率指导 | N/A |
| 输入逻辑阈值 | N/A |
| 电压降 / RDS(on)/ 饱和度 | N/A |
| 热限制 | -40 到 +85 °C |
| 包裹 | 3.6 x 3.8 毫米 |
| 备注 / 变体 | 温度和压力传感器 |
- 确保适当的电压供应:1.8V 至 3.6V 用于 BMP-180。
- 在SDA和SCL线路上使用上拉电阻,以确保稳定的I²C通信。
- 保持电线短,以避免信号衰减。
- 扫描时检查正确的 I²C 地址。
- 监测温度范围:BMP-180 的 -40 到 +85 °C。
接线说明

将BMP-180传感器和LCD显示器连接到您的Arduino,请按照以下步骤进行:

首先,连接BMP-180的Vn将引脚连接到Arduino的5V输出。接下来,连接GNDBMP-180 的引脚连接到 Arduino 的接地。SDABMP-180 的引脚应连接到 Arduino 的A4空白,虽然SCL引脚连接到A5.
对于LCD1602或LCD2004,请连接VCC将引脚连接到Arduino上的5V和GND也要将其接地。SDALCD的引脚也应该连接到A4(与 BMP-180 共享),以及SCL引脚应连接到A5.
此配置允许两个设备通过同一I²C总线进行通信,确保干净高效的设置。
代码示例与演练
要扫描 I²C 地址,我们将使用一个简单的代码片段。以下摘录初始化 I²C 通信并准备串口监视器:
#include
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial); // Leonardo: wait for serial monitor
Serial.println("\nI2C Scanner");
}
此代码初始化了用于I²C通信的Wire库,并设置了串口监视器以便输出。这对于调试和确保I²C设备被识别至关重要。
循环功能扫描I²C总线上的设备并打印它们的地址:
void loop() {
byte error, address;
int nDevices = 0;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
for(address = 1; address < 127; address++) {
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0) {
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
Serial.println(address, HEX);
nDevices++;
}
}
if (nDevices == 0) Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds for next scan
}
这个循环检查从 1 到 127 的每个地址,尝试与任何存在的设备进行通信。如果某个设备确认通信,则其地址会被打印到串行监视器。这是识别你的 LCD 或其他连接设备的 I²C 地址的关键步骤。
演示 / 期待什么
运行 I²C 扫描器时,您应该在串行监视器中看到消息,指示是否找到任何 I²C 设备。如果成功,输出将显示连接设备的地址,格式为十六进制值(例如,“在地址 0x27 找到 I2C 设备”)。如果没有找到设备,您将看到相应的消息。
确保所有连接都安全,并提供正确的电压水平以避免设备检测问题(视频中在 05:30)。
// --------------------------------------
//http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/I2cScanner
// i2c_scanner
//
// Version 1
// This program (or code that looks like it)
// can be found in many places.
// For example on the Arduino.cc forum.
// The original author is not known.
// Version 2, June 2012, Using Arduino 1.0.1
// Adapted to be as simple as possible by Arduino.cc user Krodal
// Version 3, Feb 26, 2013
// V3 by louarnold
// Version 4, March 3, 2013, Using Arduino 1.0.3
// by Arduino.cc user Krodal.
// Changes by louarnold removed.
// Scanning addresses changed from 0...127 to 1...119,
// according to the i2c scanner by Nick Gammon
// http://www.gammon.com.au/forum/?id=10896
// Version 5, March 28, 2013
// As version 4, but address scans now to 127.
// A sensor seems to use address 120.
// Version 6, November 27, 2015.
// Added waiting for the Leonardo serial communication.
//
//
// This sketch tests the standard 7-bit addresses
// Devices with higher bit addresses might not be seen properly.
// Watch Video explaining I2C address: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bqMMIbmYJS0
//
#include <Wire.h>
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial); // Leonardo: wait for serial monitor
Serial.println("\nI2C Scanner");
}
void loop()
{
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for(address = 1; address < 127; address++ )
{
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmisstion to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0)
{
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(address,HEX);
Serial.println(" !");
nDevices++;
}
else if (error==4)
{
Serial.print("Unknown error at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.println(address,HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0)
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
else
Serial.println("done\n");
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds for next scan
}|||您可能需要的东西
-
亚马逊从亚马逊购买LCD1602-I2Camzn.to
-
全球速卖通在AliExpress上购买10个LCD1602-I2Cs.click.aliexpress.com
-
全球速卖通在AliExpress购买LCD1602-I2Cs.click.aliexpress.com
资源与参考
尚无可用资源。
文件📁
Arduino 库(zip 格式)
-
LCD1602 LCD Arduino library from Robojax
robojax-LCD1602-I2C-library-master.zip0.01 MB
Fritzing 文件
-
LCD2004-I2C
LCD2004-I2C.fzpz0.02 MB














![2Pcs 5V One Channel Relay Module Low Level for SCM Control, Arduino [USA store]](https://i.ebayimg.com/images/g/SGEAAeSwuWxoyB-P/s-l225.jpg)