ESP32 Tutorial 28/55 - DHT11 Temperature Sensor with LCD | SunFounder's ESP32 IoT Learning kit
In this tutorial, we will explore how to interface the DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor with the ESP32 microcontroller. Using this setup, we will measure the ambient temperature and humidity, displaying the results on both the serial monitor and an LCD screen. Additionally, we will implement a buzzer that activates when the temperature exceeds a certain threshold.

This project not only demonstrates the use of the DHT11 sensor but also showcases the versatility of the ESP32, which includes built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a working setup that continuously monitors environmental conditions and provides real-time feedback.
For a visual guide, check out the video accompanying this tutorial (in video at 00:00). Let's dive in!
Hardware Explained
The main components used in this project are the ESP32 microcontroller, the DHT11 sensor, and an LCD display. The ESP32 will serve as the brain of the operation, processing data from the DHT11 sensor and controlling the LCD output.
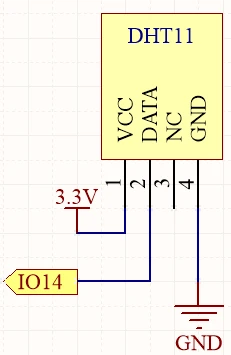
The DHT11 sensor measures humidity and temperature, providing readings through a single data line. It requires a power supply of 3.3V to 5.5V and has a low current consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered applications. The LCD will display the temperature and humidity values in real-time.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | GROVE |
|---|---|
| Part number | DHT11 |
| Logic/IO voltage | 3.3 – 5.5 V |
| Supply voltage | 3.3 V |
| Output current (per channel) | 0.5 mA typ. |
| Peak current (per channel) | 2.5 mA max. |
| PWM frequency guidance | N/A |
| Input logic thresholds | 0.3 VCC (low), 0.7 VCC (high) |
| Voltage drop / RDS(on) / saturation | Not applicable |
| Thermal limits | 0°C to 60°C |
| Package | DIP-4 |
| Notes / variants | Resolution: 1°C / 1% RH |
- Use a pull-up resistor (5 kΩ recommended) on the data line.
- Keep sensor wires short (less than 20 m) to ensure accurate readings.
- Power the DHT11 with 3.3V for optimal performance.
- Sampling period should not be less than 1 second.
- Check wiring connections if readings fail (e.g., not connected, incorrect pin).
Wiring Instructions
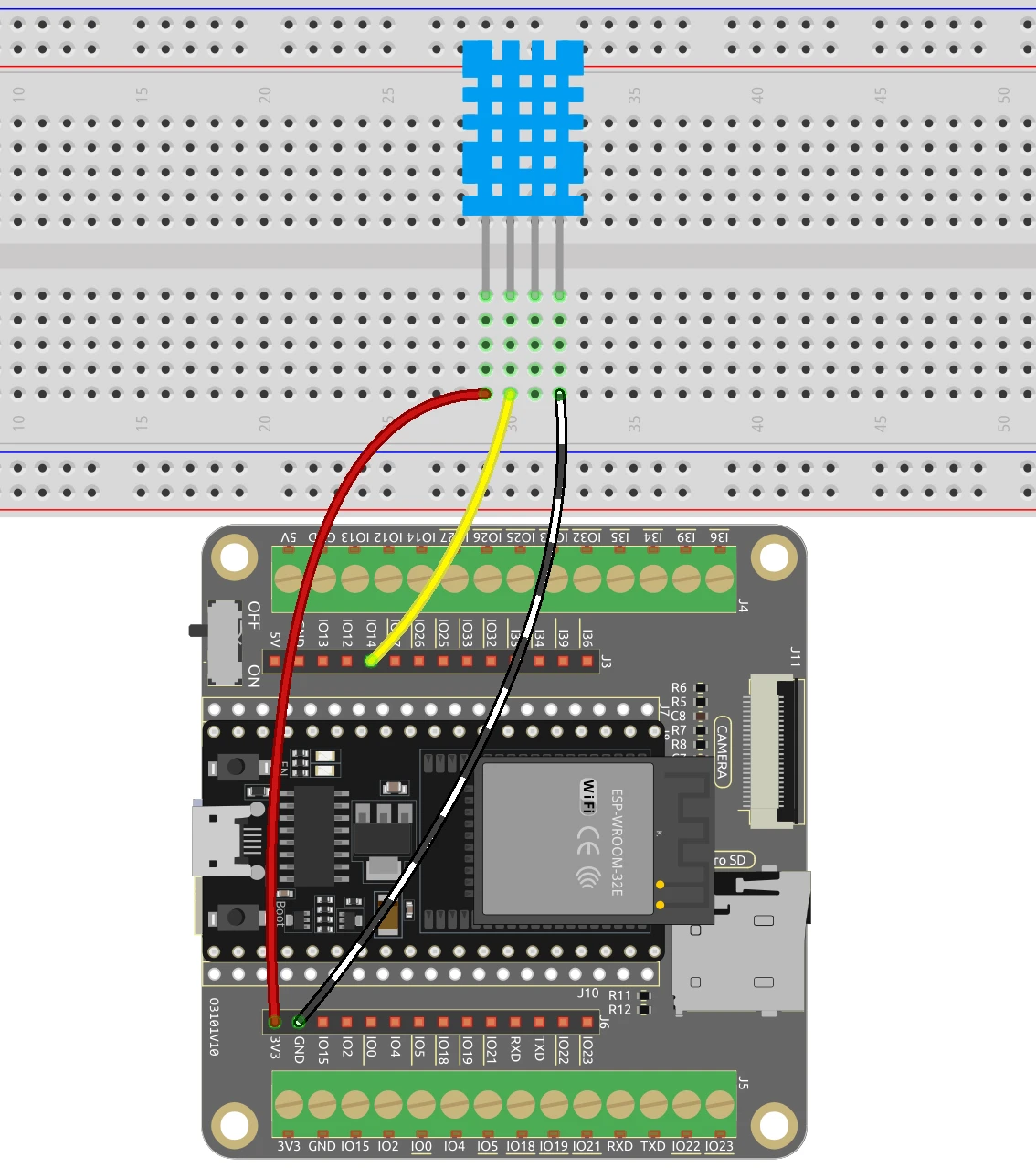

To wire the DHT11 sensor to the ESP32, start by connecting the VCC pin of the DHT11 (the leftmost pin) to the 3.3V output of the ESP32. Next, connect the ground pin (the fourth pin) to a ground (GND) pin on the ESP32. The data pin (the second pin) should be connected to GPIO pin 14 on the ESP32.
For the LCD, connect the VCC pin to the 5V output of the ESP32. The ground pin should be connected to a ground pin on the ESP32. The SDA and SCL pins of the LCD should be connected to GPIO pins 21 and 22, respectively. Ensure all connections are secure to avoid any issues while reading data.
Code Examples & Walkthrough
In the first part of the code, we initialize the DHT sensor and set the pin number with #define DHTPIN 14. This identifier allows us to easily reference the pin connected to the DHT11 data line throughout the code.
#include "DHT.h"
#define DHTPIN 14 // Set the pin connected to the DHT11 data pin
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
dht.begin();
}
In the setup() function, we initialize serial communication for debugging and begin the DHT sensor. The main loop includes a delay of 2 seconds to ensure we do not overwhelm the sensor with requests.
Next, we read the humidity and temperature values using float humidity = dht.readHumidity(); and float temperature = dht.readTemperature();. These identifiers store the measured values for later use.
void loop() {
delay(2000);
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
}
Finally, we check for any read errors and print the values to the serial monitor using Serial.print(). This allows us to observe the readings in real-time.
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.print(" %\t");
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
In the LCD code, we initialize the LCD and display the temperature and humidity on the screen using the lcd.print() function. This provides a visual representation of the data collected by the DHT11 sensor.
Demonstration / What to Expect
Once everything is wired correctly and the code is uploaded to the ESP32, you should see the temperature and humidity readings displayed on the serial monitor and the LCD screen. If the temperature exceeds 30°C, the buzzer will activate, providing an audible alert.
Be cautious of reversed connections and ensure the sensor is not exposed to extreme conditions, as it can affect the readings. You might need to adjust the threshold for the buzzer depending on your requirements (in video at 15:30).
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 Start
- 1:57 Introduction to DHT11
- 6:18 Wiring DHT11 with ESP32
- 7:67 Arduino Code explained
- 11:49 Selecting ESP32 board and COM port in Arduino IDE
- 13:30 Project demonstration
- 15:32 Getting Fahrenheit
- 16:04 displaying temperature on LCD using ESP32
- 17:20 DHT11 and LCD with ESP32 code
- 19:49 DHT11 LCD demo with ESP32
- 21:33 Taking action on Temperature value
#include "DHT.h"
#define DHTPIN 14 // 设置连接到DHT11数据引脚的引脚
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("DHT11 test!");
dht.begin();
}
void loop() {
// 在测量之间等待几秒钟。
delay(2000);
// 读取温度或湿度大约需要250毫秒!
// 传感器读取的数据可能最多会有2秒的“延迟”(这是一个非常慢的传感器)
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
// 以摄氏度(默认)读取温度
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
// 检查是否有读取失败,并提前退出(以便重试)。
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
// 打印湿度和温度
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.print(" %\t");
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
}
/*
* 这是Arduino代码,用于使用DHT11/DHT22测量温度和湿度,并在LCD屏幕上显示,由Ahmad Shamshiri为SunFounder的ESP32物联网学习套件编写。观看完整视频 https://youtu.be/qRUFZX4eDJg。本教程的完整代码、电路图和其他资源可在 https://robojax.com/RJT711 找到。
*/
#include "DHT.h"
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
#define DHTPIN 14 // 设置连接到 DHT11 数据引脚的引脚
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
// 用I2C地址0x27、16列和2行初始化LCD对象
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
void setup() {
// 以115200波特率开始串行通信
Serial.begin(115200);
// 初始化dht11
dht.begin();
// 初始化LCD
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
// 清除LCD
lcd.clear();
}
void loop() {
// 测量之间请等待几秒钟。
delay(2000);
// 读取温度或湿度大约需要250毫秒!
// 传感器读数可能会有长达2秒的“延迟”(这是一个非常慢的传感器)
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
// 以摄氏度(默认)读取温度
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
// 检查是否有任何读取失败,并提前退出(以便重试)。
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
// 在LCD上显示温度和湿度
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Temp: ");
lcd.print(temperature);
lcd.write(223); // 度数符号
lcd.print("C");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Humi: ");
lcd.print(humidity);
lcd.print("%");
}
Common Course Links
Common Course Files
|||您可能需要的东西
-
亚马逊从亚马逊购买DHT11amzn.to
-
Banggood从Banggood购买DHT11模块banggood.com
资源与参考
-
文档ESP32教程 28/55 - SunFounder DHT温度传感器文档页面docs.sunfounder.com
文件📁
Fritzing 文件
-
DHT11 Humitidy and Temperature Sensor (3 pins)
DHT11 Humitidy and Temperature Sensor (3 pins).fzpz0.20 MB
用户手册
-
DHT11 用户手册
robojax-DHT11_manual.pdf0.82 MB