ESP32 Tutorial 20/55 - Line Tracking Module | SunFounder's ESP32 IoT Learning kit
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use the ESP32 module along with the line tracking module to detect black lines on a white surface. This capability is essential for applications such as robotic cars that need to follow a designated path. Additionally, we will integrate a buzzer that activates when the line tracking module detects the black line, enhancing the feedback mechanism of our project. For further clarification, please refer to the video (in video at 0:00).
Hardware Explained
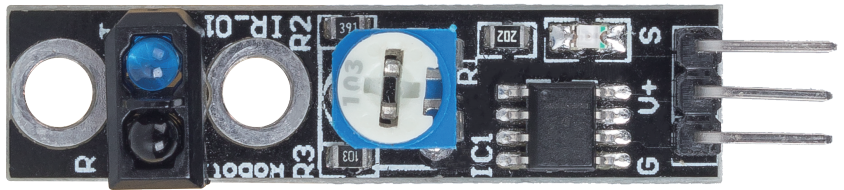
The primary components of this project include the ESP32 module, a line tracking module, and a buzzer. The ESP32 module is a powerful microcontroller featuring built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, allowing for a wide range of IoT applications. The line tracking module utilizes an infrared emitter and photoresistor to detect differences in surface color based on the intensity of the reflected infrared light.
The line tracking module operates by emitting infrared light that reflects off the surface beneath it. A darker surface, like black, absorbs more light, resulting in a lower reflected intensity, while a lighter surface, like white, reflects more light, producing a higher intensity. This difference is processed by an operational amplifier to determine the state of the surface (black or white) and output a corresponding signal.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | SunFounder |
|---|---|
| Part number | TCRT5000 |
| Logic/IO voltage | 3.3 V to 5 V |
| Output current (per channel) | 20 mA |
| Peak current (per channel) | 50 mA |
| Response time | < 10 ms |
| Detection range | 1 cm to 5 cm |
| Package | Module with header pins |
| Notes / variants | Commonly used in line following robots |
- Ensure proper power supply (3.3 V or 5 V).
- Keep the sensor clean for accurate readings.
- Adjust sensitivity using the onboard potentiometer.
- Check connections to avoid floating inputs.
- Use pull-up resistors if necessary for stable readings.
- Minimize interference from ambient infrared sources.
Wiring Instructions
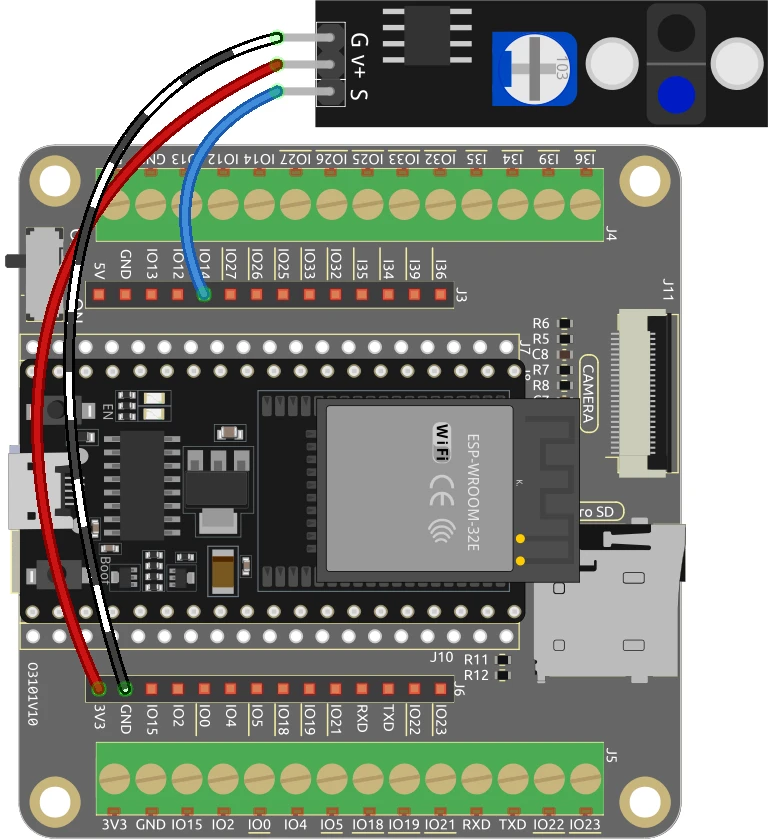
To wire the line tracking module to the ESP32, start by connecting the ground pin of the module to a ground pin on the ESP32. Then, connect the V+ pin of the line tracking module to a suitable power source, either 3.3 V or 5 V on the ESP32. The signal pin (labeled as S) should be connected to GPIO 14 on the ESP32. Ensure that these connections are secure before proceeding.
If you are using a buzzer, connect its negative terminal to the ground and the positive terminal to GPIO 27 on the ESP32. This setup allows the buzzer to activate when the line tracking module detects a black line. Make sure to double-check all connections to ensure they match the specified pins in the code.

Code Examples & Walkthrough
Below is a key excerpt from the code that sets up the line tracking module. The variable linePin is defined to represent the pin connected to the line tracking module.
const int linePin = 14; // The number of the line track module pinThis line initializes linePin as pin 14, which will be used to read the line status. The lineState variable will hold the result from the sensor.
In the setup() function, we configure the pin mode for linePin as an input.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(linePin, INPUT);
}This ensures that the ESP32 can read the state of the line tracking module. The serial communication is initiated at a baud rate of 115200 for monitoring output.
Finally, in the loop() function, we continuously read the state of the line tracking module and print the detected color.
void loop() {
lineState = digitalRead(linePin);
if (lineState == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Black");
delay(100);
} else {
Serial.println("White");
delay(100);
}
}This loop checks if the lineState is HIGH (indicating black) or LOW (indicating white) and prints the result to the serial monitor. The full code loads below the article for your reference.
Demonstration / What to Expect
Once the wiring is complete and the code is uploaded, you should observe the ESP32 printing "Black" when the line tracking module is over a black surface, and "White" when it is over a white surface. Additionally, the buzzer will sound when the module detects the black line, providing an audible alert. Be cautious of the potentiometer settings, as overly sensitive settings can lead to erratic behavior (in video at 10:00).
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 Start
- 2:22 Introduction to Line tracking module
- 5:10 Documentation page
- 9:20 Wiring explained
- 10:49 Arduino code explained
- 13:36 Selecting ESP32 board and COM port in Arduino IDE
- 15:18 Demonstration
- 18:15 Project: Line tracking with buzzer
- 19:52 Arduino code for Line tracking and buzzer
- 20:52 Demonstration
/*
* Установить номер пина
*/
const int linePin = 14; // Номер выхода модуля трековой линии
// Переменная для хранения статуса линии
int lineState = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Инициализируйте вывод модуля трековой линии как входной.
pinMode(linePin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Считайте состояние модуля трековых линий.
lineState = digitalRead(linePin);
if (lineState == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Black");
delay(100);
}
else {
Serial.println("White");
delay(100);
}
}
Common Course Links
Common Course Files
Ресурсы и ссылки
-
ДокументацияESP32 Учебник 20/55 - страница документа SunFounder для отслеживания линииdocs.sunfounder.com
Файлы📁
Нет доступных файлов.