ESP32 Tutorial 46/55 - Remote Temperature Monitoring using HiveMQ MQTT | SunFounder's ESP32 kit
In this tutorial, we will create a remote temperature monitoring system using the ESP32 and the MQTT protocol. This project allows us to publish temperature data to an MQTT broker and control an LED remotely using a web interface. By pressing a button, we can send temperature readings to the cloud, and we can also receive commands to turn the LED on or off.

The ESP32 is a powerful microcontroller that features built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making it ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. In this setup, we will use an NTC thermistor to measure temperature, a push button to trigger the readings, and an LED to indicate status. The data will be sent to HiveMQ, a popular MQTT broker, where it can be accessed remotely (in video at 00:45).
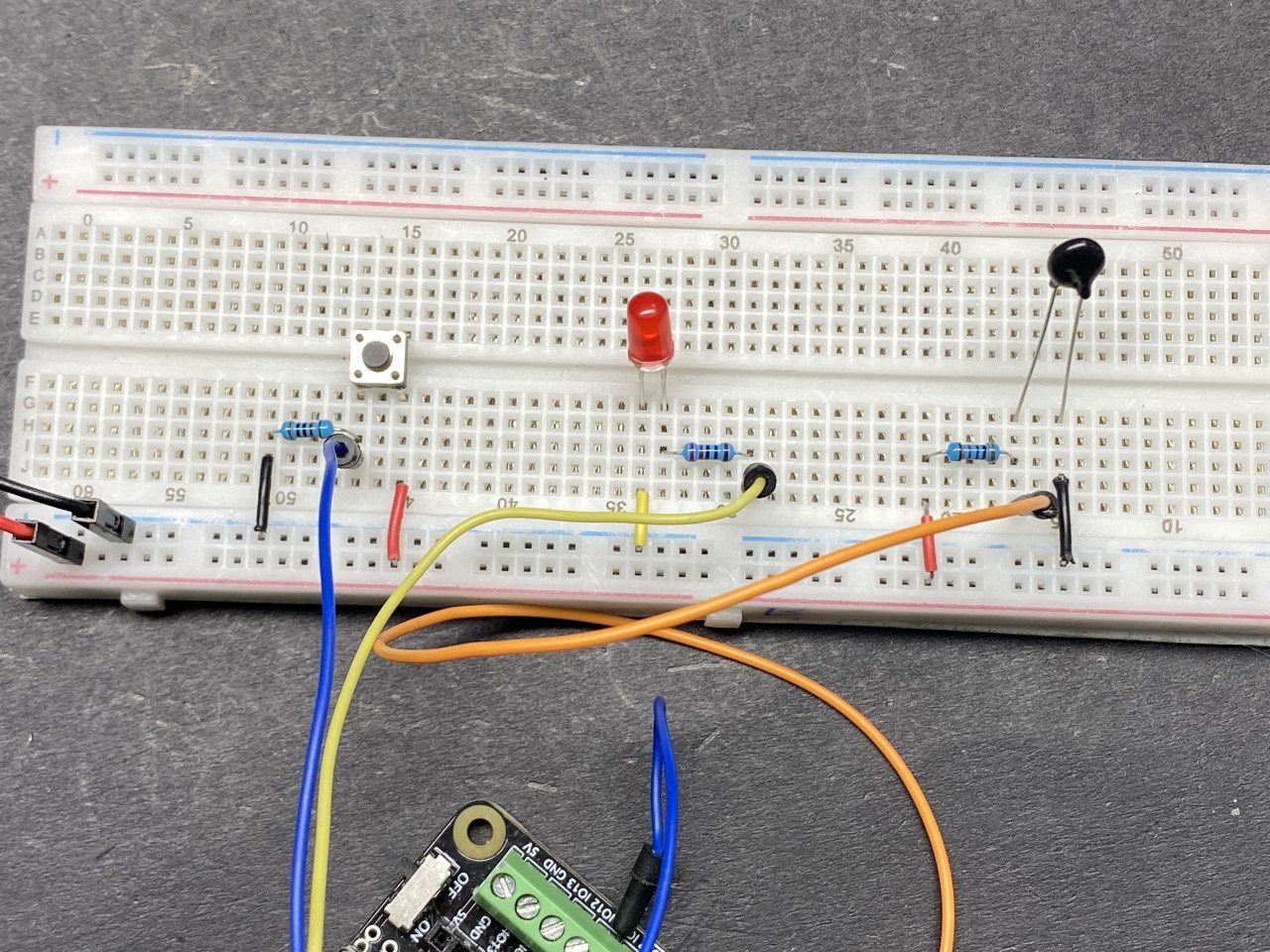
Hardware Explained
For this project, we will utilize the following components:
- ESP32 Microcontroller: This board serves as the central processing unit, handling Wi-Fi connections and MQTT communications.
- NTC Thermistor: This temperature sensor changes its resistance based on temperature. It provides an analog signal that the ESP32 can read to determine the current temperature.
- LED: This light-emitting diode will be used to indicate the status based on commands received via MQTT.
- Push Button: This button will trigger the ESP32 to read the temperature and publish it to the MQTT broker.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | SunFounder |
|---|---|
| Part number | ESP32 |
| Logic/IO voltage | 3.3 V |
| Supply voltage | 5 V (via USB) |
| Output current (per channel) | 12 mA max |
| PWM frequency guidance | Up to 40 kHz |
| Input logic thresholds | 0.3 V (low), 2.4 V (high) |
| Thermal limits | -40 to 85 °C |
| Package | ESP32-WROOM-32 |
- Ensure proper voltage levels to avoid damage.
- Use pull-up resistors for the push button to ensure stable readings.
- Decoupling capacitors can help stabilize the power supply.
- Be cautious with the thermistor's wiring to avoid incorrect readings.
- Verify your MQTT broker details for successful connection.
Wiring Instructions

To wire the components, start by connecting the NTC thermistor. Connect one pin of the thermistor to the 3.3 V supply on the ESP32. The other pin connects to pin 36 on the ESP32, and it should also connect to a 10 kΩ resistor, which is then connected to ground. This creates a voltage divider that allows the ESP32 to read the thermistor's resistance.
Next, connect the LED. The longer pin (anode) of the LED connects to pin 4 on the ESP32 through a 220 Ω resistor, while the shorter pin (cathode) connects to ground. For the push button, connect one side to 3.3 V and the other side to pin 14 on the ESP32. Additionally, connect a 10 kΩ resistor from the button pin to ground to ensure a stable LOW state when the button is not pressed.
Install Required library
The PubSubClient library is used here, you can install it from the Library Manager.

Code Examples & Walkthrough
In the setup, we initialize the serial communication, set up the Wi-Fi connection, and configure the MQTT server. Here's a snippet of the setup code:
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
setup_wifi();
client.setServer(mqtt_server, 1883);
client.setCallback(callback);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}This part of the code establishes the connection to the Wi-Fi network and sets up the MQTT server. The pin modes for the button and LED are also configured here.
The loop function continuously checks the button state and publishes temperature data when pressed. Here's a focused excerpt from the loop:
void loop() {
if (!client.connected()) {
reconnect();
}
client.loop();
if (digitalRead(buttonPin)) {
long now = millis();
if (now - lastMsg > 5000) {
lastMsg = now;
char tempString[8];
dtostrf(thermistor(), 1, 2, tempString);
client.publish("SF/TEMP", tempString);
}
}
}In this loop, we check if the ESP32 is connected to the MQTT broker. If the button is pressed, it reads the temperature from the thermistor and publishes it to the topic "SF/TEMP" every 5 seconds.
Demonstration / What to Expect
When the project is set up and running, pressing the button will publish the current temperature to the MQTT broker. You can monitor this data from any MQTT client. Additionally, you can send messages to control the LED; sending "on" will light it up, while "off" will turn it off. Watch for the expected behavior in the video at 15:30, where the temperature readings are shown after each button press.
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 Start
- 2:05 Introduction to the project
- 7:06 Free HiveMQ service
- 7:56 Wiring explained
- 11:11 Arduino code explained
- 18:46 Selecting ESP32 board and COM port in Arduino IDE
- 20:30 Demonstration of HiveMQ Free broker
/*
* :ref: https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-mqtt-publish-subscribe-arduino-ide/
* https://docs.sunfounder.com/projects/kepler-kit/en/latest/iotproject/5.mqtt_pub.html
*/
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
// #include <Wire.h>
// 用您的SSID/密码组合替换下列变量。
const char* ssid = "SSID";
const char* password = "PASSWORD";
// 添加您的 MQTT 代理地址,例如:
const char* mqtt_server = "broker.hivemq.com";
const char* unique_identifier = "sunfounder-client-sdgvsda";
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient client(espClient);
long lastMsg = 0;
int value = 0;
// LED引脚
const int ledPin = 4;
const int buttonPin = 14;
// 当你连接到WIFI时,只有36、39、34、35、32、33引脚可以用于模拟读取。
// 定义常量
const int thermistorPin = 36; // 连接到热敏电阻的引脚
const float referenceVoltage = 3.3;
const float referenceResistor = 10000; // 电阻值(10k)
const float beta = 3950; // 贝塔值(典型值)
const float nominalTemperature = 25; // 计算温度系数的名义温度
const float nominalResistance = 10000; // 在名义温度下的电阻值
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// 默认设置
setup_wifi();
client.setServer(mqtt_server, 1883);
client.setCallback(callback);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void setup_wifi() {
delay(10);
// 我们首先连接到一个WiFi网络。
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* message, unsigned int length) {
Serial.print("Message arrived on topic: ");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print(". Message: ");
String messageTemp;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Serial.print((char)message[i]);
messageTemp += (char)message[i];
}
Serial.println();
// 如果在"SF/LED"主题上收到消息,你需要检查该消息是"开"还是"关"。
// 根据消息更改输出状态。
if (String(topic) == "SF/LED") {
Serial.print("Changing state to ");
if (messageTemp == "on") {
Serial.println("on");
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else if (messageTemp == "off") {
Serial.println("off");
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
}
}
void reconnect() {
// 循环直到我们重新连接
while (!client.connected()) {
Serial.print("Attempting MQTT connection...");
// 尝试连接
if (client.connect(unique_identifier)) {
Serial.println("connected");
// 订阅
client.subscribe("SF/LED");
} else {
Serial.print("failed, rc=");
Serial.print(client.state());
Serial.println(" try again in 5 seconds");
// 请在重试之前等待5秒。
delay(5000);
}
}
}
float thermistor() {
int adcValue = analogRead(thermistorPin); // 读取ADC值
float voltage = (adcValue * referenceVoltage) / 4095.0; // 计算电压
float resistance = (voltage * referenceResistor) / (referenceVoltage - voltage); // 使用更新的配置计算热敏电阻电阻值
// 使用贝塔参数方程计算温度
float tempK = 1 / (((log(resistance / nominalResistance)) / beta) + (1 / (nominalTemperature + 273.15)));
float tempC = tempK - 273.15; // 获取摄氏温度
float tempF = 1.8 * tempC + 32.0; // 获取华氏温度
// 打印温度
Serial.print("Temp: ");
Serial.println(tempC);
delay(200); // 等待200毫秒
return tempC;
}
void loop() {
if (!client.connected()) {
reconnect();
}
client.loop();
// 如果按钮被按下,发布温度到主题 "SF/TEMP"
if (digitalRead(buttonPin)) {
long now = millis();
if (now - lastMsg > 5000) {
lastMsg = now;
char tempString[8];
dtostrf(thermistor(), 1, 2, tempString);
client.publish("SF/TEMP", tempString);
}
}
}
Common Course Links
Common Course Files
资源与参考
-
文档ESP32 教程 46/55 - SunFounder 物联网通信的 MQTT 文档页面docs.sunfounder.com
文件📁
没有可用的文件。


















