ESP32 Tutorial 54/55 - Set WS2812 LED Strip Color over Wifi | SunFounder's ESP32 IoT Learning kit
In this tutorial, we will learn how to control the color of a WS2812 RGB LED strip using an ESP32 microcontroller over Wi-Fi. By utilizing a color picker, you can select different colors from your mobile device or desktop and send that information to the LED strip. This project showcases the capabilities of the ESP32, allowing for seamless interaction with LED lighting through a web interface.

The ESP32 microcontroller is equipped with both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making it a versatile choice for IoT applications. In this project, we will focus on the Wi-Fi functionality to control the LED strip. Users will be able to choose colors dynamically, creating a visually engaging experience. For additional clarity on this project, be sure to check out the video at (in video at 00:00).
Hardware Explained
The primary components for this project include the ESP32 microcontroller and the WS2812 LED strip. The ESP32 is a powerful microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi capabilities, enabling wireless communication and control.
The WS2812 LED strip consists of individually addressable RGB LEDs, allowing you to set the color of each LED independently. Each LED incorporates a control circuit and a RGB LED within a single package, which simplifies the wiring and control of multiple LEDs.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | Worldsemi |
|---|---|
| Part number | WS2812B |
| Logic/IO voltage | 3.5–5.3 V |
| Supply voltage | 5 V |
| Output current (per channel) | 20 mA |
| Peak current (per channel) | 60 mA |
| PWM frequency guidance | 400 Hz |
| Input logic thresholds | 0.3 × VDD (low), 0.7 × VDD (high) |
| Voltage drop / RDS(on) / saturation | 0.5 V |
| Thermal limits | –40 to +80 °C |
| Package | 5050 SMD |
| Notes / variants | Available in various lengths and configurations. |
- Ensure proper power supply to avoid damaging the LEDs.
- Use a common ground between the ESP32 and the LED strip.
- Keep data lines short to prevent signal degradation.
- Consider adding a capacitor (1000 µF) across the power supply for stability.
- Use a resistor (470 Ω) on the data line for signal integrity.
Wiring Instructions
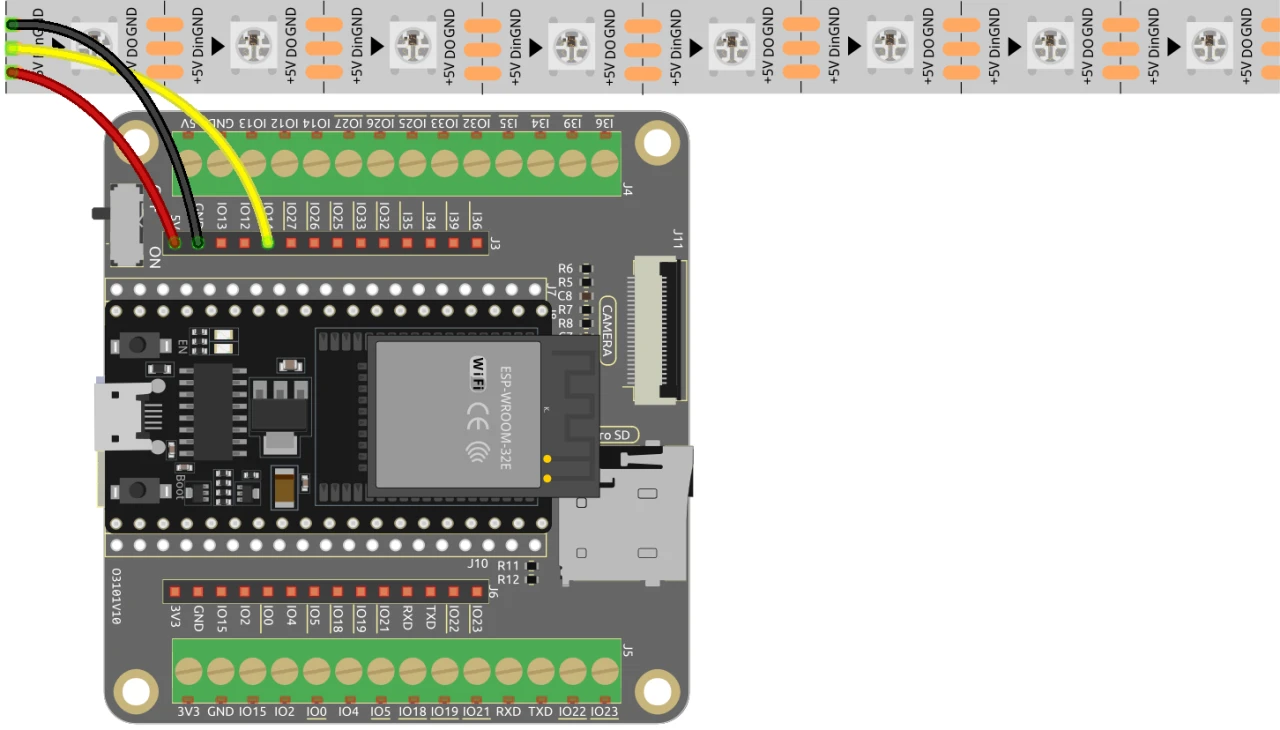
To wire the ESP32 to the WS2812 LED strip, connect the components as follows: First, connect the 5V pin of the LED strip to the 5V output of the ESP32. Next, connect the ground (GND) pin of the LED strip to a GND pin on the ESP32. Finally, connect the data pin of the LED strip (usually labeled as DI or Data In) to GPIO pin 13 on the ESP32. Make sure all connections are secure to ensure proper functionality.
In the video, alternative wiring methods are briefly mentioned, but the setup described here is the recommended configuration for optimal performance (in video at 03:00).
Code Examples & Walkthrough
The code begins by including the necessary libraries for controlling the WS2812 LED strip and setting up the web server. The LED pin is defined as LED_PIN and the number of LEDs in the strip is set with NUM_LEDS.
#define LED_PIN 13 // NeoPixel LED strip
#define NUM_LEDS 8 // Number of LEDs
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
This snippet initializes the NeoPixel library and sets up the LED strip on the specified pin. The Adafruit_NeoPixel object, strip, is what you will use to control the LED colors.
Next, the code initializes Wi-Fi and sets up a web server to handle incoming requests. The SSID and password for the network are defined, allowing the ESP32 to connect to the Wi-Fi.
const char *ssid = "your_SSID";
const char *password = "your_PASSWORD";
WebServer server(80);
In this excerpt, replace your_SSID and your_PASSWORD with your actual Wi-Fi credentials. This connection enables the ESP32 to communicate with devices on the same network, allowing for remote control of the LED strip.
The main function for changing the LED color is setColor(), which iterates through each LED and sets its color based on the selected RGB values.
void setColor() {
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, valueR, valueG, valueB); // Set the color of the i-th LED
strip.show(); // Update the LED strip with the new colors
delay(10); // Wait for 10 milliseconds
}
}
This function ensures that each LED in the strip is updated with the selected color. The delay allows the LEDs to change color smoothly. As you interact with the web interface, this function will be called to reflect your color choices.
Demonstration / What to Expect
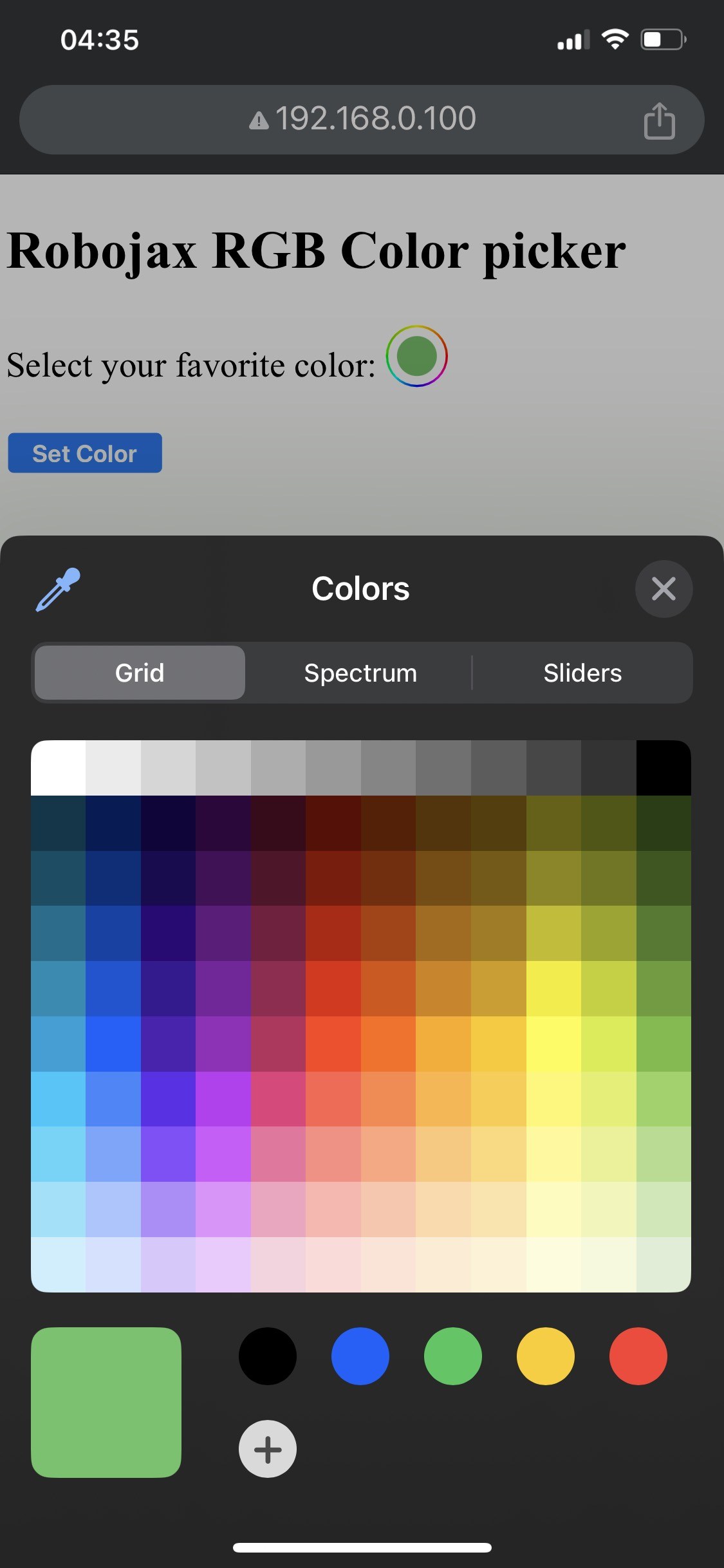

When the setup is complete, you should be able to access the web interface via the ESP32's IP address. You will see a color picker that allows you to select any color, which will then be sent to the LED strip. If the ESP32 loses Wi-Fi connection, the strip will blink a warning color, indicating the issue (in video at 14:30).
Common pitfalls include incorrect wiring, which can lead to the LEDs not lighting up, or using incorrect SSID/password combinations that prevent the ESP32 from connecting to the network. Always double-check your connections and credentials.
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 Start
- 2:01 Introduction to the project
- 3:09 Docs
- 3:47 RGB color explained
- 7:47 Wiring
- 8:40 Arduino code for WS2812 with WIFI explained
- 19:35 Selecting ESP32 board and COM port in Arduino IDE
- 21:17 Controlling LED Strip over wifi demo
/*
* 通过ESP32使用WiFi控制RGB LED
*
* 完整视频说明 https://youtu.be/J_UFHk_T9aE
* 📚⬇️ 下载和资源页面 https://robojax.com/RJT687
* 作者:Ahmad Shamshiri 2023年12月18日
*
* 观看该视频的视频说明:
*
* 我将Adafruit的DHT库与ESP8266 WebServer结合在一起,两个链接如下:
* Adafruit DHT库在GitHub上:https://github.com/adafruit/DHT-sensor-library
* 以及
* ESP8266在GitHub上:https://github.com/esp8266/Arduino
*
* 版权 © 2015,Majenko Technologies
* 版权所有。
*
* 在符合以下条件的情况下,允许以源代码和二进制形式重新分发和使用,带或不带修改:
*
* 源代码的再分发必须保留上述版权声明、此条件列表以及以下免责声明。
*
* 二进制形式的再分发必须在随分发提供的文档和/或其他材料中重现上述版权声明、此条件列表以及以下免责声明。
*
* 未经特别事先书面许可,不得使用Majenko Technologies的名称或其贡献者的名称来认可或推广基于此软件的产品。
*
* 本软件由版权持有者和贡献者按“原样”提供,任何明示或暗示的担保,包括但不限于对适销性和特定用途适用性的暗示担保均被否认。在任何情况下,版权持有者或贡献者均不对因使用本软件而导致的任何直接、间接、偶然、特别、惩戒性或后果性损害负责(包括但不限于替代商品或服务的采购;使用、数据或利润的损失;或业务中断),无论因何原因,包括合同、严格责任或侵权(包括过失或其他方式)而导致,甚至在被告知可能发生此类损害的情况下。
*/
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> // 包括 Adafruit NeoPixel 库
#define LED_PIN 13 // NeoPixel LED灯条
#define NUM_LEDS 8 // LED的数量
// 创建 Adafruit_NeoPixel 类的实例
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
// LED灯带的初始颜色
int valueR = 178; // 红色范围从0到255
int valueG = 27; // 从 0 到 255 的绿色
int valueB = 84; // 蓝色范围从 0 到 255
bool showSerialData = false;
String theColorR, theColorG, theColorB;
String theColor ="ff0000";
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiClient.h>
#include <WebServer.h>
#include <ESPmDNS.h>
const char *ssid = "dars";
const char *password = "hhhhhhhhhhh";
WebServer server(80);
void showColorPicker() {
String page = "<!DOCTYPE html>\n";
page +="<html>\n";
page +="<body>\n";
page +="<div style=\"zoom: 300%;\">\n";
page +="<h2>Robojax RGB Color picker</h2>\n";
page +="<p id=\"result\"></p>\n";
page +="<form action=\"/color\">\n";
page +=" <label for=\"favcolor\">Select your favorite color:</label>\n";
page +=" <input type=\"color\" id=\"favcolor\" name=\"favcolor\" value=\"#";
page += theColor;
page +="\"><br><br>\n";
page +=" <input type=\"submit\" value=\"Set Color\" />\n";
page +="</form> \n</div>\n";
page +="</body>\n";
page +="</html>\n";
server.send(200, "text/html", page);
}
// 从 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44683071/convert-string-as-hex-to-hexadecimal
uint64_t StrToHex(const char* str)
{
return (uint64_t) strtoull(str, 0, 16);
}
void getColor(){
// server.send(200, "text/plain", message);
if(server.argName(0) == "favcolor")
{
String newColor = String(server.arg(0)); // 获取GET参数0并将其转换为字符串
theColor = newColor.substring(1); // 移除颜色前面的 # 符号,如 #B2a48d。
theColorR = newColor.substring(1, 3); // 从 #B2a48d 中提取 B2 作为示例
theColorG = newColor.substring(3, 5); // 从 #B2a48d 中提取 a4 作为例子
theColorB = newColor.substring(5, 7); // 从 #B2a48d 中提取 8d 作为例子
valueR = StrToHex(theColorR.c_str()); // 将字符串转换为R的十六进制
valueG = StrToHex(theColorG.c_str()); // 将字符串转换为G的十六进制
valueB = StrToHex(theColorB.c_str()); // 将字符串转换为 B 的十六进制形式
if(showSerialData)
{
Serial.print("valueR: ");
Serial.println(valueR);
Serial.print("valueG: ");
Serial.println(valueG);
Serial.print("valueB: ");
Serial.println(valueB );
}
}
showColorPicker(); // 确保颜色选择器显示。
// server.send(200, "text/plain", message);
}
void setColor()
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, valueR, valueG, valueB); // 将第i个LED的颜色设置为红色
strip.show(); // 更新LED灯条,使用新颜色。
delay(10); // 等待100毫秒
}
}
void noConnection()
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, 255, 45, 0); // 将第i个LED的颜色设置为红色
strip.show(); // 更新LED灯条,使用新颜色。
delay(50); // 等待100毫秒
}
delay(200);
for (int i = NUM_LEDS-1; i >=0; i--) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, 0, 255, 180); // 将第i个LED的颜色设置为红色
strip.show(); // 更新LED灯条,使用新颜色。
delay(50); // 等待100毫秒
}
}
void handleNotFound() {
String message = "File Not Found\n\n";
message += "URI: ";
message += server.uri();
message += "\nMethod: ";
message += (server.method() == HTTP_GET) ? "GET" : "POST";
message += "\nArguments: ";
message += server.args();
message += "\n";
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < server.args(); i++) {
message += " " + server.argName(i) + ": " + server.arg(i) + "\n";
}
server.send(404, "text/plain", message);
}
void setup_wifi() {
delay(10);
// 我们首先连接到一个WiFi网络。
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.println("");
// 等待连接
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
noConnection();
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Connected to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
Serial.print("Open: http: // ");
Serial.print(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println(" to read temperature");
if (MDNS.begin("robojaxRGB")) {
Serial.println("MDNS responder started");
}
}
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
strip.begin(); // 初始化 NeoPixel 灯带
strip.show(); // 将初始颜色设置为黑色
setup_wifi();
server.on("/", showColorPicker); // 显示带有颜色选择器的主页
// server.on("/color", setColor);//更改WS2812 RGB LED的颜色
server.on("/color", HTTP_GET, getColor);
server.on("/inline", []() {
server.send(200, "text/plain", "this works as well");
});
server.onNotFound(handleNotFound);
server.begin();
Serial.println("HTTP server started");
}
void loop(void) {
// Robojax.com
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
setup_wifi();
}
server.handleClient();
// showColorPicker();
setColor();
delay(300); // 如果不需要经常读取,请将此更改为更大的值(1000或更多)。
// Robojax.com 代码用于 ESP32 和 DHT11 DHT22
}
Common Course Links
Common Course Files
资源与参考
尚无可用资源。
文件📁
没有可用的文件。


















