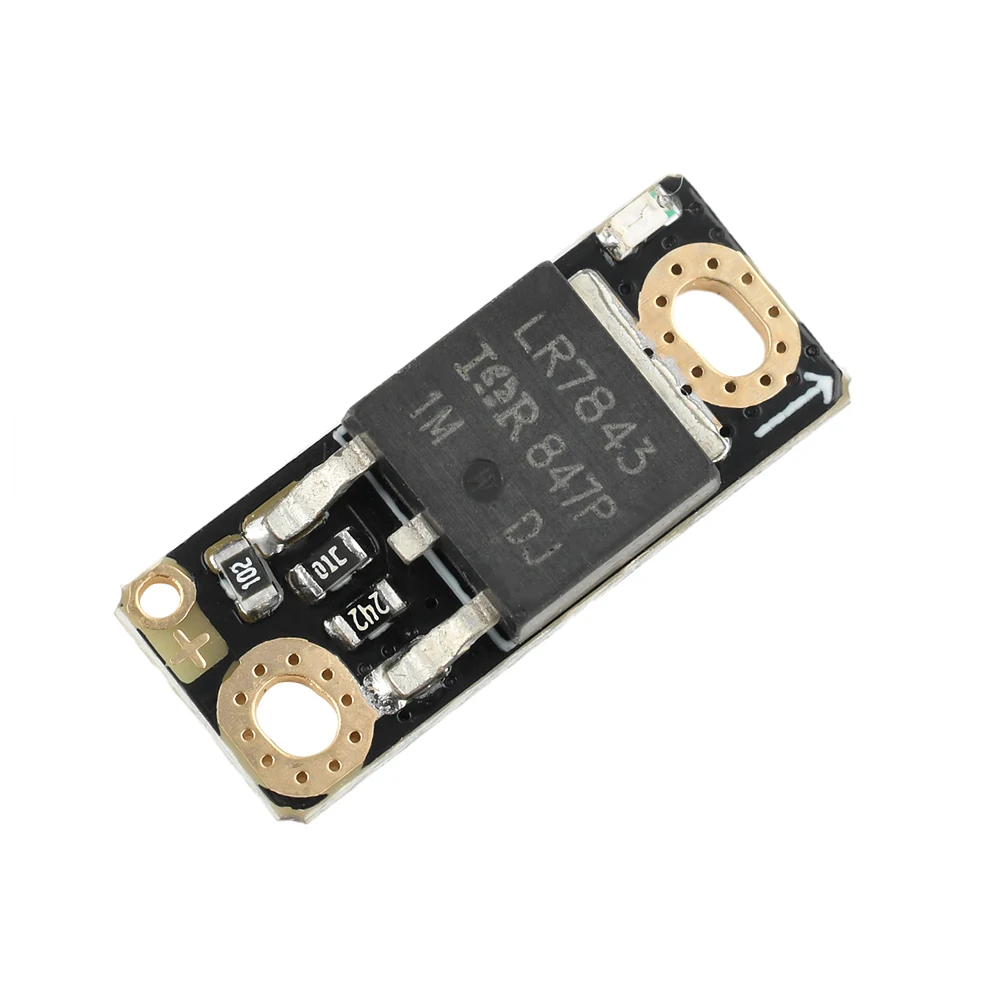
Project: RJMD-R2101 H-Bridge MOSFET Motor Driver
In this tutorial, we will explore how to control a DC motor using the RJMD-R2101 H-Bridge MOSFET motor driver. This project will demonstrate how to effectively utilize the IRFZ44N MOSFETs in conjunction with the IR2101 gate drivers to control motor speed and direction. By the end of this guide, you will have a functional motor control setup that can accelerate, brake, and stop the motor smoothly.

As we progress, we will cover the necessary hardware components, wiring instructions, and example code snippets to clarify how everything works together. For a more visual representation, I recommend watching the associated video (in video at 02:15).

Hardware Explained
The primary components in this project are the IR2101 gate driver and the IRFZ44N MOSFETs. The IR2101 is a high-speed driver designed for driving N-channel MOSFETs in a half-bridge configuration. It allows for efficient switching and control of the MOSFETs, enabling the motor to run smoothly.
The IRFZ44N MOSFETs act as the switching elements that control the power delivered to the motor. When activated by the IR2101, these MOSFETs can handle high currents, providing the necessary power to drive the motor. Together, these components allow for precise control over motor direction and speed.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | International Rectifier |
|---|---|
| Part number | IRFZ44N |
| Logic/IO voltage | 10 V (VGS) |
| Supply voltage | 55 V (VDS) |
| Output current (per channel) | 49 A (max) |
| Peak current (per channel) | 120 A (max) |
| PWM frequency guidance | up to 100 kHz |
| Input logic thresholds | 2.0 V (VGS(th)) |
| Voltage drop / RDS(on) / saturation | 0.025 Ω (max) |
| Thermal limits | 175 °C (max) |
| Package | TO-220 |
| Notes / variants | Commonly used in H-Bridge configurations |
- Ensure proper heat sinking for the MOSFETs to prevent overheating.
- Use PWM for speed control to achieve smooth motor operation.
- Verify the power supply voltage does not exceed MOSFET ratings.
- Ensure correct polarity when wiring the motor to avoid damage.
- Use decoupling capacitors near the power supply to stabilize voltage.
Wiring Instructions

To wire the RJMD-R2101 motor driver, start by connecting the power supply. Connect the VCC pin of the driver to a 5V power source. The GND pin should be connected to the ground of the power supply. Next, connect the control pins: the PWM signal for the first MOSFET should go to pin PWM1_HIN1_PIN (which is pin 9), and the enable pin for the first MOSFET should connect to EN1_LIN1_PIN (pin 8). For the second MOSFET, connect the PWM signal to PWM2_HIN2_PIN (pin 3) and the enable pin to EN2_LIN2_PIN (pin 2).

Make sure to connect the motor terminals to the appropriate outputs of the H-Bridge. If you are using Arduino, connect the PWM pins to the designated pins on the Arduino board. For example, connect PWM1_HIN1_PIN to pin 9, EN1_LIN1_PIN to pin 8, and so forth. This setup will allow you to control the motor effectively.
Code Examples & Walkthrough
The code section includes functions to control motor speed and direction using the defined pins. Below is an excerpt from the motor control sketch:
const int PWM1_HIN1_PIN= 9; // PWM pin for first MOSFET
const int EN1_LIN1_PIN= 8; // Enable pin for first MOSFET
In this part, we define the pins used for controlling the first MOSFET. The PWM1_HIN1_PIN is used for speed control, while the EN1_LIN1_PIN enables the motor driver.
void Motor(boolean direction, int speed=0) {
int speedPWM = map(speed, 0, 100, 0, 255);
// Control motor direction and speed here
}
This function takes in a direction parameter to determine whether the motor should spin clockwise or counterclockwise. The speed parameter is mapped to a PWM value, allowing for smooth control over motor speed.
void stop() {
digitalWrite(EN1_LIN1_PIN, LOW); // Disable first MOSFET
}
The stop function disables the motor by setting the enable pin low, effectively stopping any current flow through the motor. This ensures a quick stop without damaging the components.
For the full code, please refer to the complete program loaded below the article.
Demonstration / What to Expect
When the setup is complete, you should observe the motor responding to the commands sent from the Arduino. The motor will spin in the specified direction, and you can adjust the speed using PWM signals. Common issues to watch for include reversed polarity connections, which may cause the motor to run in the opposite direction, and floating inputs that could lead to erratic behavior.
During testing, you may also notice the motor speed changing based on the PWM values sent. Ensure all connections are secure to avoid interruptions in power flow, which could affect performance (in video at 05:45).
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 - Introduction to the project
- 02:15 - Overview of hardware components
- 05:45 - Demonstration of motor control
- 08:30 - Code walkthrough and explanation
Images
Resources & references
-
External
-
ExternalIR2101 Gate Driver Datasheetinfineon.com
-
ExternalIRFZ44N MOSFET datasheetinfineon.com
Files📁
Other Files
-
RJMD-R2101_H-Bridge_Motor_Driver_Manufacturing_Pack.zipH-Bridge MOSFET Motor Driver all three files that you may need to place order. Contains: PCB Layers Gerber zip, BMO excel file and coordinate file
application/zip0.17 MB