Arduino Code and Video for the HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
In this tutorial, we will explore how to use the HC-SR04 ultrasonic distance sensor with an Arduino. The HC-SR04 is an economical and effective way to measure distances using ultrasonic waves. By sending a signal and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return, we can calculate the distance to an object accurately.

This project involves setting up the sensor with an Arduino and writing a simple program to read and display the distance measurements. The program will utilize the NewPing library to streamline communication with the sensor. If you want a visual reference or further clarification on any steps, be sure to check the video (in video at 00:00).
Hardware Explained
The HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor consists of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits ultrasonic pulses at a frequency above the human hearing range, while the receiver listens for the echo of those pulses after they bounce off an object. By calculating the time between sending the pulse and receiving the echo, we can determine the distance to the object.
The sensor has two essential pins: the trigger pin and the echo pin. The trigger pin is used to initiate the measurement by sending a short high signal, while the echo pin receives the reflected signal and measures the time it takes for the echo to return.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | HC-SR04 |
|---|---|
| Part number | HC-SR04 |
| Logic/IO voltage | 5 V |
| Supply voltage | 5 V |
| Output current (per channel) | 15 mA |
| Peak current (per channel) | 20 mA |
| PWM frequency guidance | N/A |
| Input logic thresholds | 0.3 V (low), 0.7 V (high) |
| Voltage drop / RDS(on) / saturation | N/A |
| Thermal limits | 0°C to 70°C |
| Package | Module |
| Notes / variants | Maximum range 400 cm |
- Ensure proper power supply (5 V).
- Keep the sensor clean for accurate readings.
- Use the trigger pin to initiate measurements.
- Do not exceed the maximum distance for reliable results.
- Maintain a clear path for ultrasonic waves to reflect back.
- Use decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins.
- Be cautious about ambient noise that may interfere with readings.
- Test different distances to familiarize yourself with the sensor.
Wiring Instructions

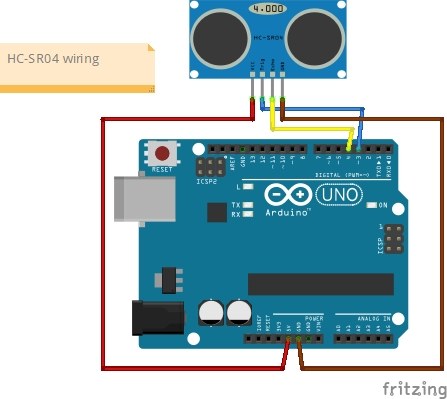
To wire the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to your Arduino, follow these steps:
- Connect the
VCCpin of the HC-SR04 to the 5V pin on the Arduino. - Connect the
GNDpin of the HC-SR04 to a ground pin on the Arduino. - Connect the
TRIGpin of the HC-SR04 (which is usually blue) to digital pin 12 on the Arduino. - Connect the
ECHOpin of the HC-SR04 (which is usually green) to digital pin 11 on the Arduino.
Ensure that the connections are secure to avoid any intermittent readings. If you are using a different setup or have alternative wiring, refer to the video for additional guidance (in video at 00:00).
Code Examples & Walkthrough
The following code initializes the NewPing library and sets up the pins for the HC-SR04 sensor. The main components include defining the trigger and echo pins, as well as the maximum distance.
#define TRIGGER_PIN 12 // Trigger pin
#define ECHO_PIN 11 // Echo pin
#define MAX_DISTANCE 200 // Max distance in cm
NewPing sonar(TRIGGER_PIN, ECHO_PIN, MAX_DISTANCE); // Set up NewPingIn this excerpt, the TRIGGER_PIN and ECHO_PIN are set to digital pins 12 and 11, respectively. The MAX_DISTANCE is defined as 200 cm, which is the maximum distance you are interested in measuring.
Next, we have the setup function where the serial monitor is initialized to display the results:
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial monitor
}This code opens the serial communication at a baud rate of 115200, allowing us to see the distance measurements in the serial monitor.
Finally, the loop function measures the distance and checks if it is less than or equal to 12 cm:
void loop() {
delay(50); // Wait between pings
int distance = sonar.ping_cm(); // Measure distance
if(distance <=12){ // Check distance
Serial.println("Very close"); // Print if very close
}
}In the loop(), we introduce a delay of 50 milliseconds to control the frequency of measurements. The distance is measured, and if it is less than or equal to 12 cm, it prints "Very close" to the serial monitor.
For the complete code, please refer to the loading section below the article.
Demonstration / What to Expect
When you run the program, the Arduino will continuously measure the distance to the nearest object. It should print the distance in centimeters and notify you with "Very close" when an object is detected within 12 cm. If the object is too close, you may get inaccurate readings or no readings at all, as noted in the video (in video at 10:00).
Ensure that the sensor is positioned correctly and that there are no obstacles blocking the ultrasonic waves. If everything is set up properly, you should see consistent measurements displayed in the serial monitor.
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 - Introduction to the HC-SR04
- 01:30 - Wiring the sensor
- 03:00 - Overview of the code
- 05:00 - Running the program
- 07:30 - Measuring distances
Things you might need
-
eBay
-
BanggoodPurchase HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor from Banggoodbanggood.com
Resources & references
-
ExternalHC-SR04 Ultrasonic Library from the Arduino official websiteplayground.arduino.cc
Files📁
No files available.


















