How to Control DC Motors with an ESP32 and L298N Module over Wi-Fi
Control Two DC Motors Over Wi-Fi with ESP32 and L298N
This tutorial demonstrates how to build a powerful and responsive system to control two DC motors using an ESP32 microcontroller and an L298N motor driver module. You will be able to start, stop, change the speed, and reverse the direction of each motor independently through a web page hosted by the ESP32. This web interface can be accessed from any device with a web browser, like a phone or computer, as long as it's connected to the same Wi-Fi network.
Components Overview
- ESP32: A powerful microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi, making it perfect for web-based control projects.
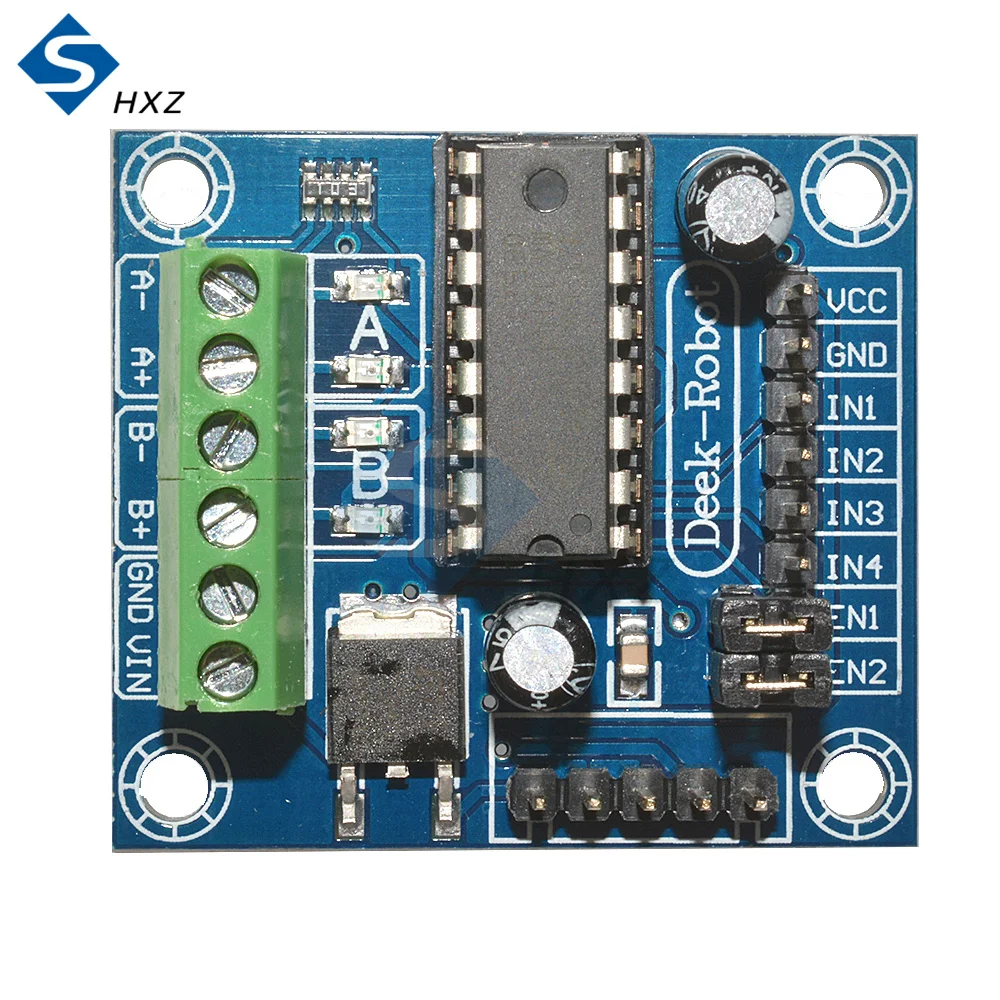
- L298N Motor Driver: A versatile and affordable dual H-bridge motor driver capable of controlling two DC motors. It can handle a wide voltage range, up to 35 volts, making it suitable for most hobbyist motors used in smart cars and robotics.
- Robojax Library: To simplify the code, we use a custom Robojax library designed for the L298N driver that works with the ESP32.
Wiring Guide
The wiring for this project connects the ESP32 to the L298N driver, which in turn connects to the motors and a power source. The full wiring is explained in the video starting at 05:05.
Power Connections
- External Power: Connect your motor power supply (e.g., 7.2V to 35V) to the L298N's screw terminals. The positive wire goes to the `+12V` (or VMS) terminal, and the negative wire goes to the `GND` terminal.
- Powering the ESP32: The L298N module has an onboard 5V voltage regulator. Once you provide external power, this regulator generates a stable 5V, which is available at the `+5V` terminal. You can use this to power your ESP32 by connecting a wire from the L298N's `+5V` terminal to the ESP32's `5V` (or Vin) pin. This eliminates the need for a separate power supply for the microcontroller.
- Common Ground: It is essential to have a common ground. Connect a wire from the L298N's `GND` terminal to a `GND` pin on the ESP32.
Control Pin Connections
Connect the six control pins from the L298N to the ESP32 as follows. These pins control the speed and direction of the two motors.
- Motor 1 (L298N Side A):
- `ENA` connects to ESP32 pin 19 (Speed Control)
- `IN1` connects to ESP32 pin 18 (Direction Control)
- `IN2` connects to ESP32 pin 5 (Direction Control)
- Motor 2 (L298N Side B):
- `ENB` connects to ESP32 pin 4 (Speed Control)
- `IN3` connects to ESP32 pin 17 (Direction Control)
- `IN4` connects to ESP32 pin 16 (Direction Control)
Arduino IDE & Library Setup
Before uploading the code, you need to prepare your Arduino IDE to work with the ESP32. The setup process is detailed in the video at 07:41.
The link to use in the "preferences" of the Arduino IDE for the ESP32 board is:
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json
Watch the video for instructions.
- Add ESP32 Board URL: Go to File > Preferences. In the "Additional Boards Manager URLs" field, you need to paste the official JSON URL for ESP32 boards.
- Install ESP32 Boards: Open the Boards Manager (Tools > Board > Boards Manager), search for "esp32", and install the package provided by Espressif Systems.
- Select Board & Port: Go to Tools > Board and select a suitable board like "ESP32 Rover Module". Then, go to Tools > Port and select the COM port that your ESP32 is connected to. You can find the correct port number in your computer's Device Manager.
- Install Robojax Library: You must download the Robojax L298N library, which will be available as a .zip file. In the Arduino IDE, go to Sketch > Include Library > Add .ZIP Library... and select the downloaded file to install it.
User-Customizable Code Settings
The provided code is designed to be easy to use. You only need to configure a few parameters at the top of the file to match your setup and preferences. This is explained starting at 12:20.
Wi-Fi Credentials
You must change these two lines to match your local Wi-Fi network's name (SSID) and password. Remember that the SSID is case-sensitive.
const char *ssid = "YourWifiName";
const char *password = "YourWifiPassword";Library Initialization (Debug Mode)
The code offers two options for initializing the library. For troubleshooting, you can enable debug mode, which prints detailed status information to the Serial Monitor. For normal operation, use the line without debugging to save resources. To switch, simply comment one line and uncomment the other.
// for two motors without debug information
//Robojax_L298N_DC_motor motor(IN1, IN2, ENA, CHA, IN3, IN4, ENB, CHB);
// for two motors with debug information
Robojax_L298N_DC_motor motor(IN1, IN2, ENA, CHA, IN3, IN4, ENB, CHB, true);Motor Behavior Parameters
You can set the default behavior for each motor independently.
// MOTOR 1 SETTINGS
int motor1Direction = CW; // Default direction: CW or CCW
const int motor1changeStep = 10; // Speed change per click (e.g., 10%)
int motor1Speed = 40; // Initial speed when the page loads (0-100)
const int motor1MinimumSpeed = 20; // The minimum speed the motor will run at
const int motor1MaximumSpeed = 100; // The maximum speed the motor will run at
int motor1StopState = HIGH; // Motor state on load: HIGH=Stopped, LOW=Running
// MOTOR 2 SETTINGS
int motor2Direction = CW;
const int motor2changeStep = 10;
int motor2Speed = 60;
const int motor2MinimumSpeed = 20;
const int motor2MaximumSpeed = 100;
int motor2StopState = HIGH;Live Project in Action
After uploading the code, open the Arduino Serial Monitor and press the reset button on the ESP32. The ESP32 will connect to your Wi-Fi and print its IP address.
Type this IP address into the browser of a phone or computer that is connected to the same Wi-Fi network. The control page will load, showing controls for both motors. You can use the buttons to increase or decrease speed, change direction, and start or stop each motor. The web interface will update in real-time to show the current status (speed, direction, and running/stopped state) of each motor.
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 - Introduction & Final Project Demo
- 02:02 - L298N Module Overview
- 05:05 - Wiring Guide
- 07:41 - Arduino IDE Setup for ESP32
- 09:49 - Robojax Library Installation
- 12:20 - Explanation of User-Customizable Code Settings
- 22:46 - Live Project Demonstration
Resources & references
Files📁
Other files
-
Robojax ESP32 DC Motor LibraryThis is library to control DC motor only
robojax_ESP-L298N-DC-Motor_library.zip0.18 MB