Extracting Latitude and Longitude from a GPS Signal in Arduino
In this tutorial, we will learn how to extract latitude and longitude data from a GPS signal using the Arduino and the Ublox NEO-6M GPS module. This project is particularly useful for applications that require location tracking, such as robotics or outdoor navigation. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a working program that reads GPS data and prints the coordinates to the serial monitor.

Before we dive into the details, you may want to refer to the associated video for further clarification on the wiring and code implementation (in video at 00:00).
Hardware Explained
The primary component for this project is the Ublox NEO-6M GPS module. This module is designed to provide accurate positioning data using signals from GPS satellites. It can receive signals from multiple satellites simultaneously, which allows for precise location tracking. The module communicates with the Arduino using serial communication, making it easy to integrate into various projects.
In addition to the GPS module, you will need an Arduino board to process the GPS data. The Arduino will read the data sent by the GPS module and extract the latitude and longitude values for further use. The GPS module typically operates at 5V, and it provides a serial output that the Arduino can read through its RX pin.
Datasheet Details
| Manufacturer | u-blox |
|---|---|
| Part number | NEO-6M |
| Logic/IO voltage | 3.3V |
| Supply voltage | 3.0 to 5.5V |
| Output current | ≤ 50 mA |
| GPS sensitivity | -165 dBm |
| Operating temperature | -40 to 85 °C |
| Update rate | 1 Hz (default) |
| Package | 25 x 35 x 4 mm |
| Notes / variants | Various configurations available |
- Ensure that the GPS module is connected to a stable power source (3.0 to 5.5V).
- Use a suitable library to handle the GPS data parsing.
- Keep the antenna clear of obstructions for better satellite reception.
- Check the baud rate of the GPS module; it typically operates at 9600 baud.
- Consider using a capacitor for power smoothing if the GPS module is unstable.
Wiring Instructions
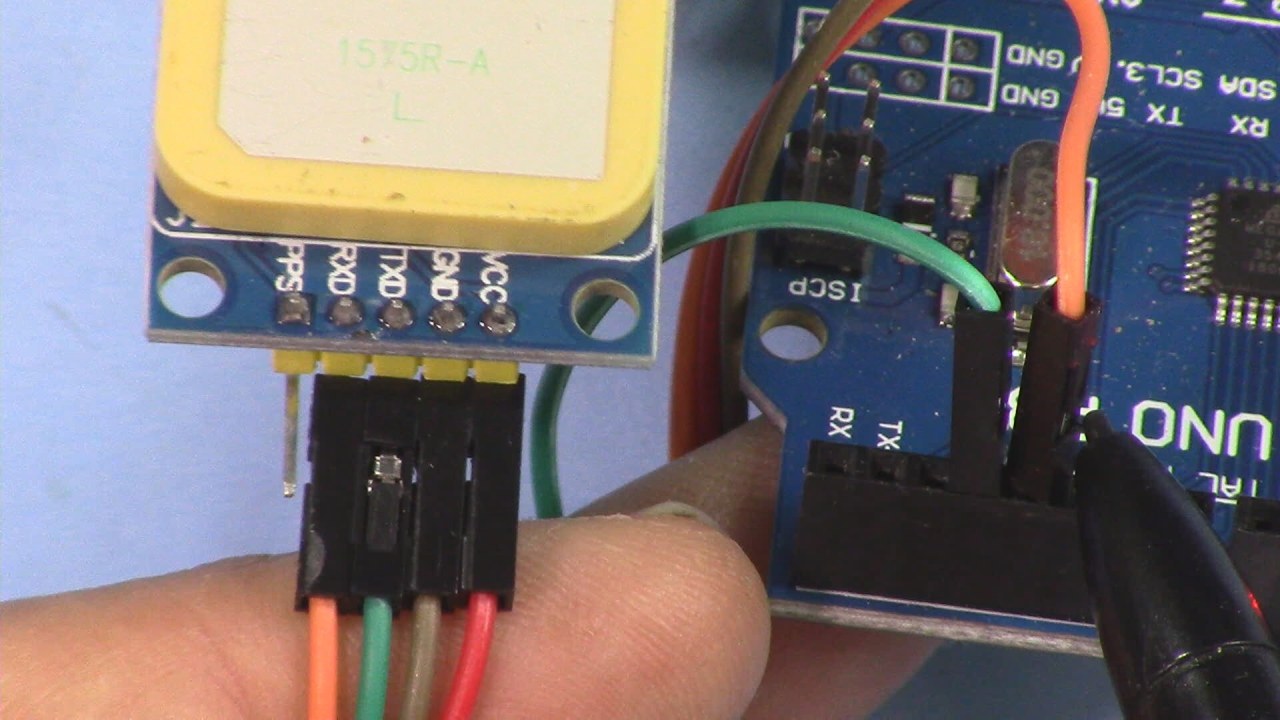
To wire the NEO-6M GPS module to your Arduino, start by connecting the VCC pin of the GPS module to the 5V pin on the Arduino. Next, connect the GND pin of the GPS module to the ground (GND) pin on the Arduino. The GPS module will communicate with the Arduino using the TX and RX pins. Connect the TX pin of the GPS module to the RX pin (usually pin 0) on the Arduino.
If you are using an Arduino with dedicated I2C pins, ensure to connect the SDA and SCL pins appropriately (typically A4 for SDA and A5 for SCL on standard Arduino boards). After wiring, double-check all connections to ensure that they are secure and properly oriented.
Code Examples & Walkthrough
Here's a short excerpt from the code to initialize the serial communication and set up the input string for GPS data:

void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
inputString.reserve(200);
}This code initializes the serial communication at a baud rate of 9600 and reserves space for the incoming GPS data string.
Next, let's look at the part of the code that processes the incoming GPS data and extracts latitude and longitude:
if (BB == signal) {
String LAT = inputString.substring(7, 17);
String LON = inputString.substring(20, 31);
Serial.println(LAT);
Serial.println(LON);
}In this snippet, the program checks if the incoming data matches the expected GPS signal. If it does, it extracts the latitude and longitude values from the input string and prints them to the serial monitor.
Finally, the code includes a section to handle new data arriving via the serial connection:
void serialEvent() {
while (Serial.available()) {
char inChar = (char) Serial.read();
inputString += inChar;
if (inChar == '\\n') {
stringComplete = true;
}
}
}This function reads incoming characters from the serial port and appends them to the inputString. Once a newline character is detected, it sets the stringComplete flag to true, indicating that a complete string of data has been received.
Demonstration / What to Expect
Upon uploading the code and running the Arduino, you should see the latitude and longitude values printed in the serial monitor. It's important to ensure that the GPS module has a clear view of the sky to receive satellite signals effectively. If the module does not receive a signal, it may not display valid coordinates (in video at 02:30).
Common pitfalls include wiring errors, insufficient power supply, and poor satellite reception. Make sure to troubleshoot these aspects if you encounter any issues.
Video Timestamps
- 00:00 - Introduction
- 02:30 - Wiring instructions
- 05:00 - Code explanation
- 08:15 - Demonstration of GPS functionality
Resources & references
No resources yet.
Files📁
No files available.


















